̈ Chapter 11: Wireless LAN – WLAN LANCOM Reference Manual LCOS 3.50
257
Wireless LAN – WLAN
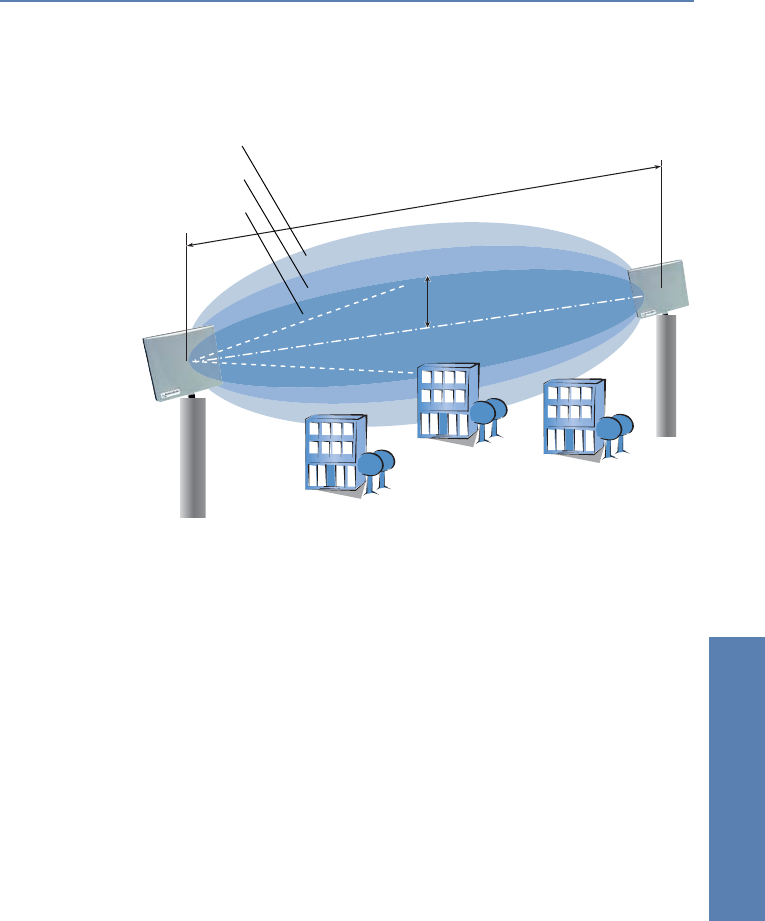
transmitter and receiver. The areas where the waves amplify or cancel
themselves out are known as Fresnel zones.
To ensure an optimal signal reception between transmitter and receiver, the
Fresnel zone 1 should remain free from any obstruction. Any disturbances
from elements protruding into this zone will significantly reduce the effective
signal power. The object not only screens off a portion of the Fresnel zone, but
the resulting reflections also lead to a significant reduction in the signal
reception.
The radius (R) of Fresnel zone 1 is calculated with the following formula
assuming that the signal wavelength (
λ) and the distance between
transmitter and receiver (d) are known.
R = 0.5 *
√ (λ * d)
The wavelength in the 2.4-GHz band is approx. 0.125m, in the 5-GHz band
approx. 0.05 m.
Example: With a separating distance of 4 km between the two antennae, the
radius of Fresnel zone 1 in the 2.4-GHz band is 11 m, in the 5-GHz band 7 m.
Fresnel zone 1
Fresnel zone 2
Fresnel zone 3
D
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
d
Radius R


















