LANCOM Reference Manual LCOS 3.50 ̈ Chapter 14: Virtual Private Networks—VPN
334
Virtual Private Networks—
VPN
packet. The comparison with the sent ICV of the packet determines the
integrity and authenticity of the packet.
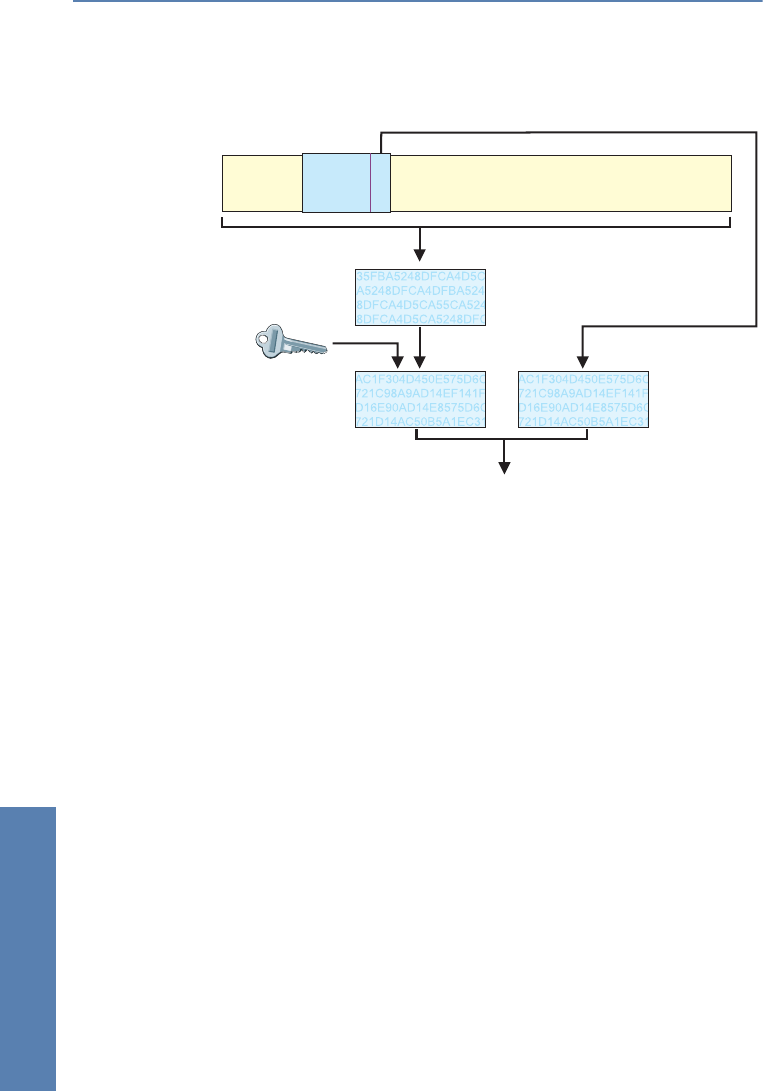
Determining the checksum for the integrity check
AH adds a checksum to each packet before it is sent to guarantee the integrity
of the transferred packets. At the recipients end, AH checks whether the
checksum and the contents of the package match. If this is not the case, the
packet was either incorrectly transferred or deliberately manipulated. Such
packets are discarded immediately and are not forwarded to higher protocol
levels.
A variety of so-called hash algorithms are available to determine the
checksum. Hash algorithms are distinguished by the fact that their results (the
hash code) are a unique fingerprint of the original data. Conversely, the
original data cannot be determined on the basis of the hash code. In addition,
minimum changes of the input value entail a completely different hash code
with a high-grade hash algorithm. Systematic analyses of several hash codes
thus are made more difficult.
LANCOM VPN supports the two most common hash algorithms: MD5 and
SHA-1. Both methods work without keys, i.e. on the basis of fixed algorithms.
Keys do not play a role until a later step of AH: the final generation of the
authentication data. The integrity checksum is only a necessary intermediate
result on the way there.
IP header
AH header Data
Authentication data,
ICV
Checksum
(hash code)
ቢ
ባ
ብ
ቤ
Authentication data,
ICV
ቤ
Identical?


















