̈ Chapter 7: Routing and WAN connections LANCOM Reference Manual LCOS 3.50
65
Routing and WAN
connections
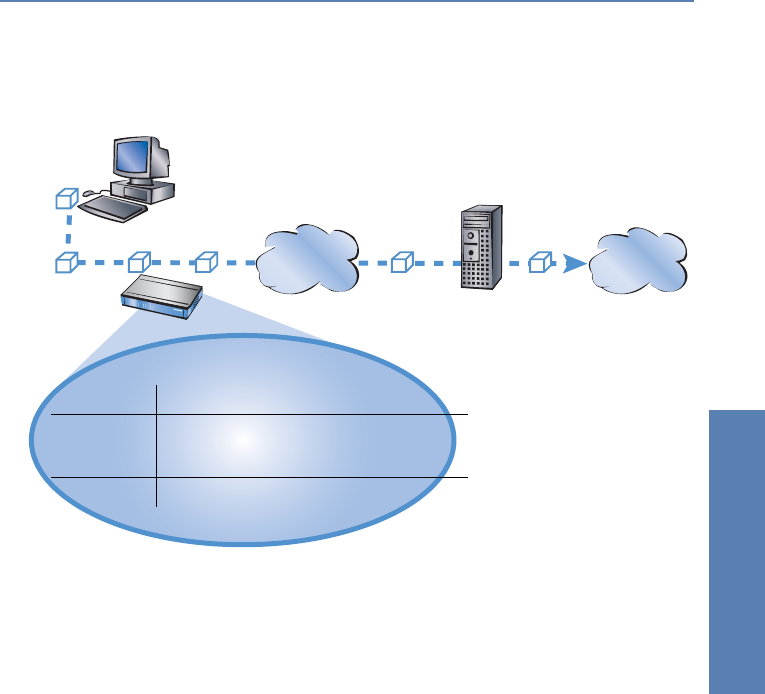
A simplified example will clarify this process. Here we assume that the IP
address of the computer being searched for is known in the Internet.
ቢ Selecting the correct route
A data packet from a computer initially finds the path to the Internet
through the IP address of the receiver. The computer sends the packet
with this address over the LAN to the router. The router determines the
remote station in its IP routing table via which the target IP address can
be reached, e.g. 'Provider_A'.
ባ Connection data for the remote station
Using these names, the router checks the names list and finds the neces-
sary connection data for provider A. Included in these connection data
are, for instance, the WAN interface (DSL, ISDN) through which the pro-
vider is connected to, protocol information, or the necessary number for
an ISDN call connection. The router also obtains the user name and pass-
word required for login from the PPP list.
ቤ Establishing the WAN connection
The router can then establish a connection to provider via a WAN inter-
face. It authenticates itself with a user name and password.
Provider
Internet user's PC
LANCOM
Data packet with
IP target address
DSL/ISDN/
ADSL
Internet
IP routing tab. IP address
Î remote station name
Name-list Remote station Îinterface, connection parame-
ters (ISDN: telephone number), communications
layer
PPP-list Terminal
Î user name and password


















