2-1
CHAPTER 2
ARCHITECTURAL OVERVIEW
This chapter describes architectural differences between the 87C196CB and the 8XC196NT.
Both the 8XC196NT and the 87C196CB are designed for high-speed calculations and fast I/O.
With the addition of the CAN (controller area network) peripheral, the 87C196CB reduces point-
to-point wiring requirements, making it well-suited to automotive and factory automation appli-
cations.
The 87C196CB is available in either an 84-pin or a 100-pin package. The 84-pin 87C196CB, like
the 8XC196NT, has up to 20 external address lines, enabling access to 1 Mbyte of linear address
space. The 100-pin 87C196CB has four additional pins available for external address lines. With
all 24 external address lines connected, the 100-pin 87C196CB can access 16 Mbytes of linear
address space.
2.1 DEVICE FEATURES
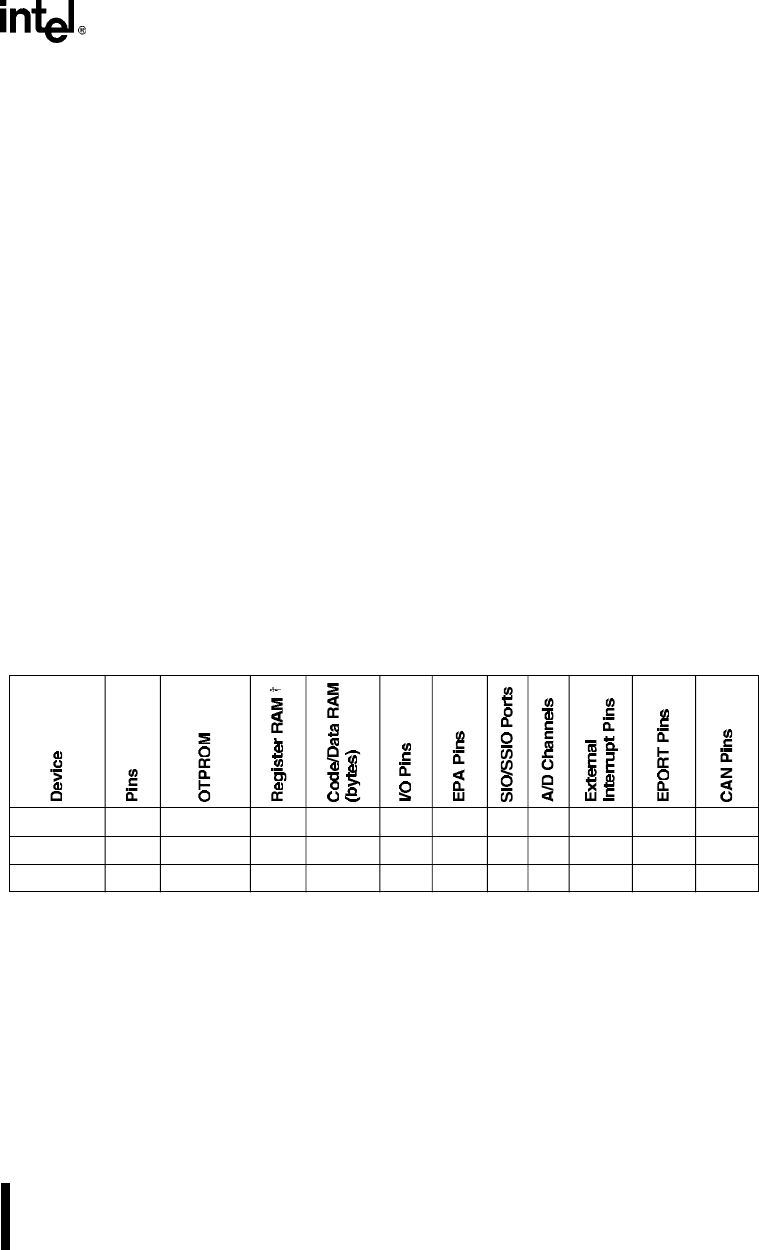
Table 2-1 lists the features of the 8XC196NT and the 87C196CB. The 87C196CB implements
more OTPROM, more register RAM, four additional A/D channels, and the CAN peripheral. The
100-pin 87C196CB also implements four additional EPORT pins.
Table 2-1. Features of the 8XC196NT and 87C196CB
8XC196NT 68 0 or 32 K 1 K 512 56 10 2 4 1 4 0
87C196CB 84 56 K 1.5 K 512 56 10 2 8 1 4 2
87C196CB 100 56 K 1.5 K 512 60 10 2 8 1 8 2
†
Register RAM amount includes the 24 bytes allocated to the core SFRs and stack pointer.


















