87C196CB SUPPLEMENT
7-10
7.3.5 Bit Timing
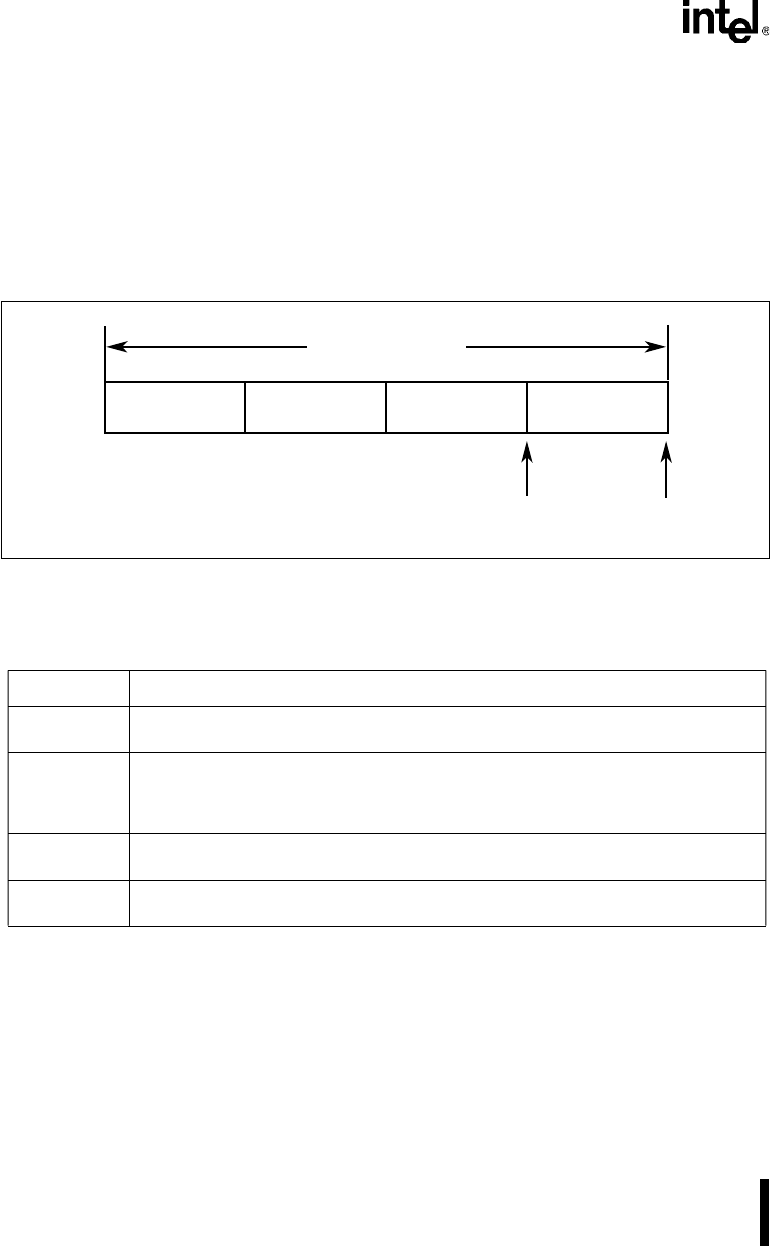
A message object consists of a series of bits transmitted in consecutive bit times. The CAN pro-
tocol specifies a bit time composed of four separate, nonoverlapping time segments: a synchro-
nization delay segment, a propagation delay segment, and two phase delay segments (Figure 7-4
and Table 7-8). The CAN controller implements a bit time as three segments, combining
PROP_SEG and PHASE_SEG1 into t
TSEG
1
(Figure 7-5 and Table 7-9). This implementation is
identical to that of the 82527 CAN peripheral.
Figure 7-4. A Bit Time as Specified by the CAN Protocol
Table 7-8. CAN Protocol Bit Time Segments
Symbol Definition
SYNC_SEG The synchronization delay segment allows for synchronization of the various nodes on
the bus. An edge is expected to lie within this segment.
PROP_SEG The propagation delay segment compensates for the physical delay times within the
network. It is twice the sum of the signal’s propagation time on the bus line, the input
comparator delay, and the output driver delay. The factor of two accounts for the
requirement that all nodes monitor all bus transmissions for errors.
PHASE_SEG1 This segment compensates for edge phase errors. It can be lengthened or shortened by
resynchronization.
PHASE_SEG2 This segment compensates for edge phase errors. It can be lengthened or shortened by
resynchronization.
SYNC_SEG
PROP_SEG
PHASE_SEG2
PHASE_SEG1
Sample Transmit
Nominal Bit Time
A2603-01


















