7-17
CAN SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
7.4.4 Programming a Message Acceptance Filter
The mask registers provide a method for developing an acceptance filtering strategy. Without a
filtering strategy, a message object could accept an incoming message only if their identifiers
were identical. The mask registers allow a message object to ignore one or more bits of incoming
message identifiers, so it can accept a range of message identifiers.
The standard global mask register (Figure 7-9) applies to messages with standard (11-bit) mes-
sage identifiers, while the extended global mask register (Figure 7-10) applies to messages with
extended (29-bit) identifiers. The message 15 mask register (Figure 7-11) provides an additional
filter for message object 15, to allow it to accept a greater range of message identifiers than mes-
sage objects 1–14 can. Clear a mask bit to accept either a zero or a one in that position.
The CAN controller applies the appropriate global mask to each incoming message identifier and
checks for an acceptance match on message objects 1–14. If no match exists, it then applies the
message 15 mask and checks for a match on message object 15.
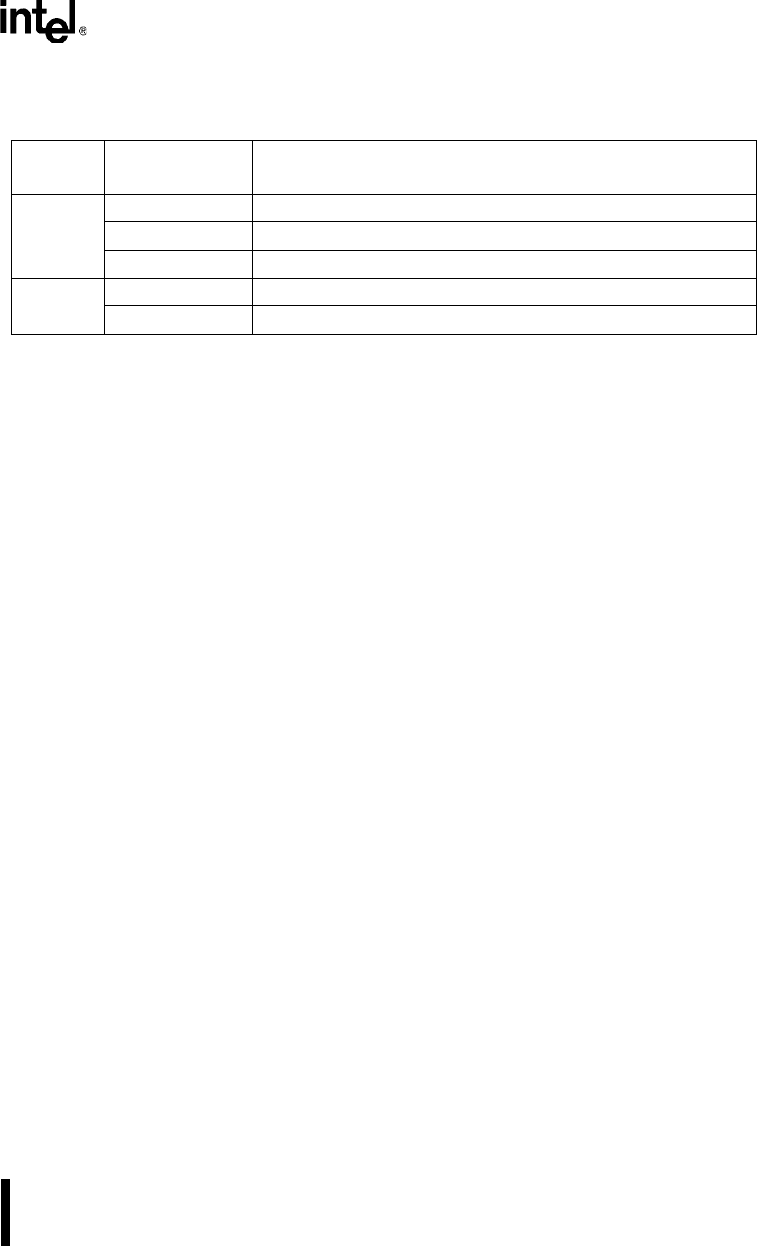
Table 7-11. Bit Timing Requirements for Synchronization
Bit Time
Segment
Requirement Comments
t
TSEG1
≥ 3tq minimum tolerance with 1tq propagation delay allowance
≥ t
SJW
+ t
PROP
for single-sample mode
≥ t
SJW
+ t
PROP
+ 2tq for three-sample mode
t
TSEG2
≥ 2tq minimum tolerance
≥ t
SJW
if t
SJW
> t
TSEG2
, sampling may occur after the bit time


















