25
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
1
1.3 About the PID Operation
1.3.3 Proportional action (P-action)
1.3.3 Proportional action (P-action)
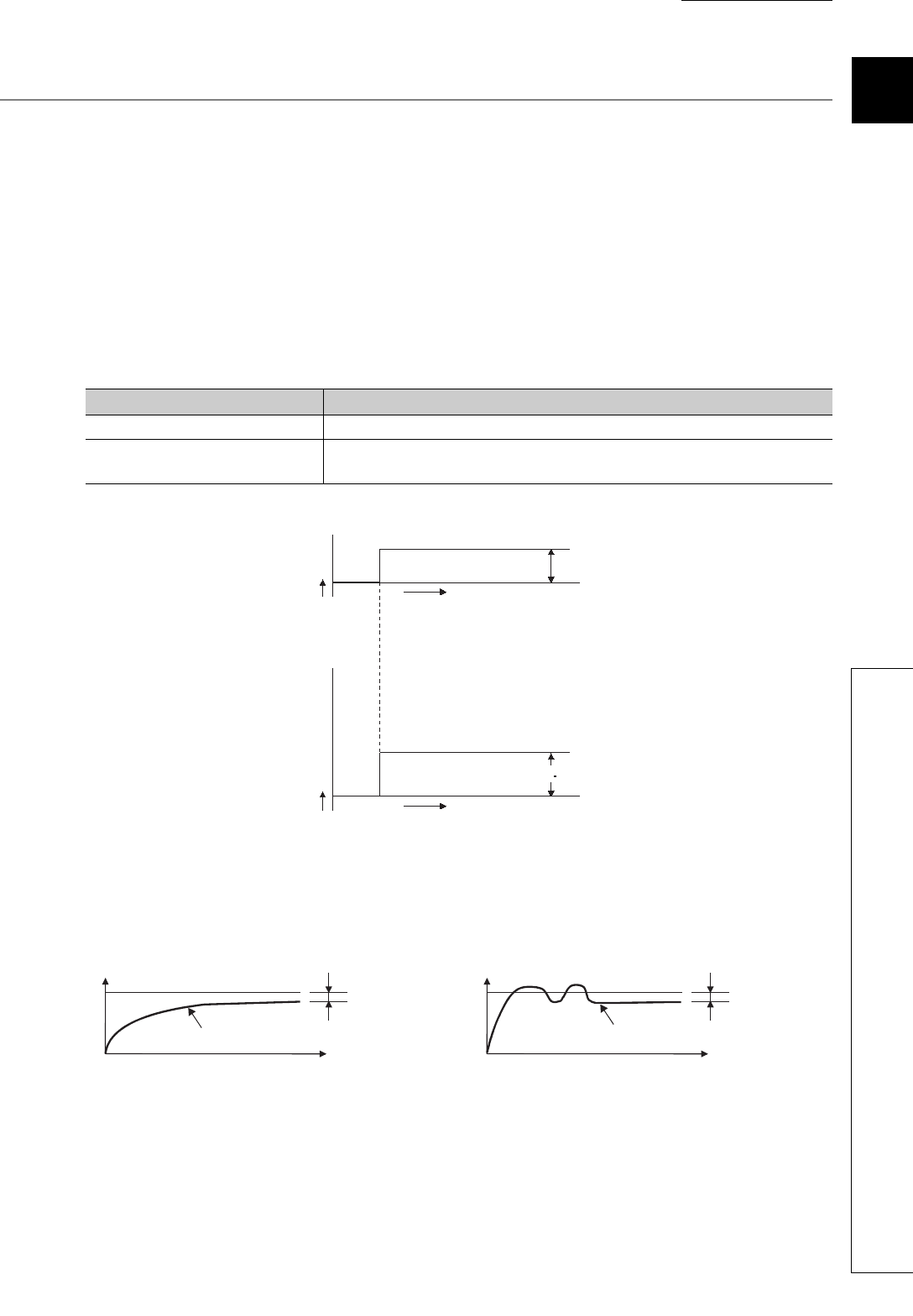
A proportional action is an action to obtain the manipulated value (MV) proportional to the deviation (difference
between the set value (SV) and the process value (PV)).
(1) Proportional gain
In a proportional action, the relationship between changes in the deviation (E) and the manipulated value can be
expressed in the following formula:
MV = K
P•E
where Kp is a proportional constant and is called proportional gain. The manipulated value (MV) varies in the
range from -5.0% to 105.0%.
The following table describes the difference of actions depending on the value of Kp, proportional gain.
The following figure shows a proportional action of step responses where the deviation (E) is a fixed value.
(2) Offset
The certain amount of difference generates between the temperature process value (PV) and the set value (SV)
is called an offset (remaining deviation).
In an proportional action, an offset (remaining deviation) generates.
Condition Proportional action
Kp is a small value The control action slows down.
Kp is a large value
The control action speeds up, though the temperature process value (PV) tends to
fluctuate around the set value.
E
Time
Time
Deviation
(E)
Manipulated
value (MV)
K
P E
Set value
(SV)
Set value
(SV)
Temperature process value (PV) Temperature process value (PV)
Offset
TimeTime
Offset