Dimension ES-2008 Ethernet Switch
IP Subnetting O
“borrowing”) determines the number of hosts you can have on
each subnet.
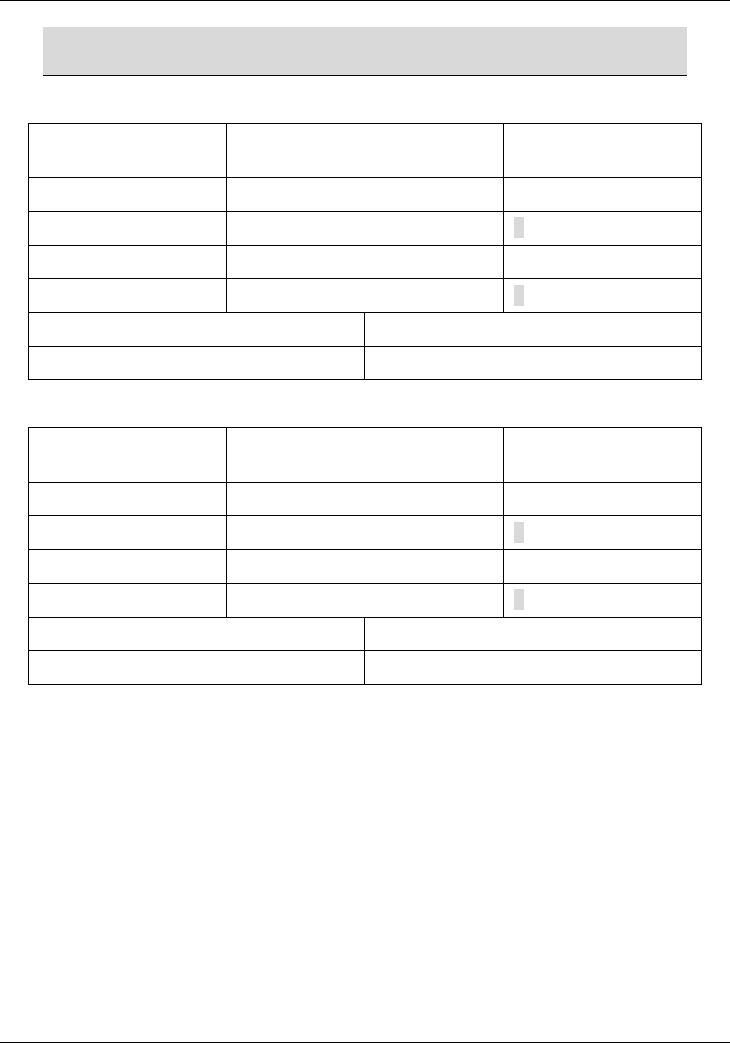
Chart 5 Subnet 1
NETWORK NUMBER LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
IP Address 192.168.1. 0
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001.
00000000
Subnet Mask 255.255.255. 128
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111.
10000000
Subnet Address: 192.168.1.0 Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.1
Broadcast Address: 192.168.1.127 Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.126
Chart 6 Subnet 2
NETWORK NUMBER LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
IP Address 192.168.1. 128
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001.
10000000
Subnet Mask 255.255.255. 128
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111.
10000000
Subnet Address: 192.168.1.128 Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.129
Broadcast Address: 192.168.1.255 Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.254
The remaining 7 bits determine the number of hosts each subnet can have. Host IDs of all
zeros represent the subnet itself and host IDs of all ones are the broadcast address for that
subnet, so the actual number of hosts available on each subnet in the example above is 2
7
– 2 or 126 hosts for each subnet.
192.168.1.0 with mask 255.255.255.128 is the subnet itself, and 192.168.1.127 with mask
255.255.255.128 is the directed broadcast address for the first subnet. Therefore, the
lowest IP address that can be assigned to an actual host for the first subnet is 192.168.1.1
and the highest is 192.168.1.126. Similarly the host ID range for the second subnet is
192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.254.
Example: Four Subnets
The above example illustrated using a 25-bit subnet mask to divide a class “C” address
space into two subnets. Similarly to divide a class “C” address into four subnets, you need
to “borrow” two host ID bits to give four possible combinations of 00, 01, 10 and 11. The