Web
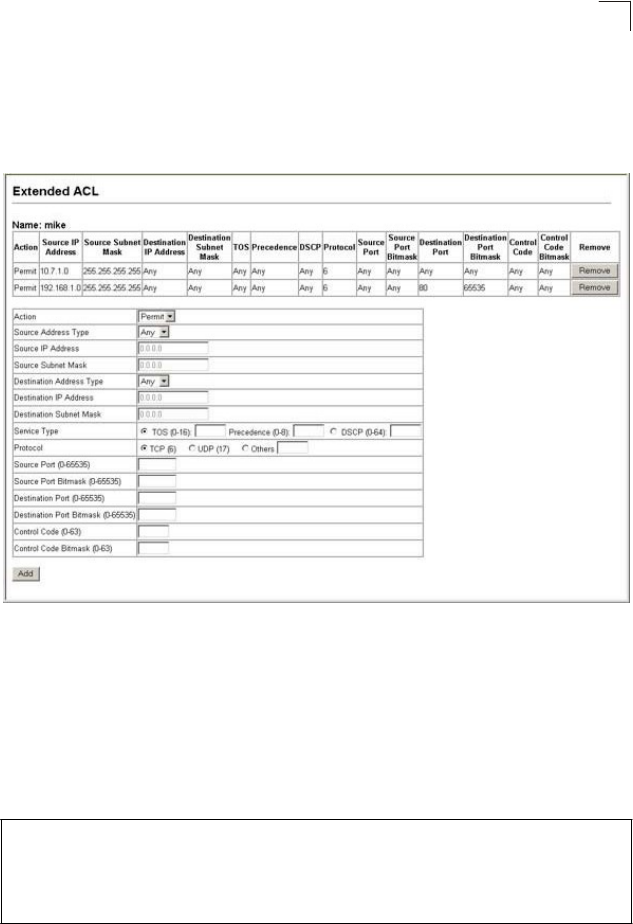
– Specify the action (i.e., Permit or Deny). Specify the source and/or
destination addresses. Select the address type (Any, Host, or IP). If you select
“Host,” enter a specific address. If you select “IP,” enter a subnet address and the
mask for an address range. Set any other required criteria, such as service type,
protocol type, or TCP control code. Then click Add.
Figure 7-3 ACL Configuration - Extended IPv4
CLI
– This example adds three rules:
1. Accept any incoming packets if the source address is in subnet 10.7.1.x. For
example, if the rule is matched; i.e., the rule (10.7.1.0 & 255.255.255.0) equals
the masked address (10.7.1.2 & 255.255.255.0), the packet passes through.
2. Allow TCP packets from class C addresses 192.168.1.0 to any destination
address when set for destination TCP port 80 (i.e., HTTP).
3. Permit all TCP packets from class C addresses 192.168.1.0 with the TCP control
code set to “SYN.”
7
Configuring Access Control Lists
Console(config-ext-acl)#permit 10.7.1.1 255.255.255.0 any
Console(config-ext-acl)#permit tcp 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 any
destination-port 80
Console(config-ext-acl)#permit tcp 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 any
control-flag 2 2
Console(config-std
-
a
cl)#
26-3
7-5


















