endpoint connecting the common transit area to the backbone itself. (Note that you
cannot configure a virtual link that runs through a stub or NSSA area.)
Virtual links can also be used to create a redundant link between any area and the
backbone to help prevent partitioning, or to connect two existing backbone areas
into a common backbone.
Any area disconnected from the backbone must include the transit area ID and the
router ID for a virtual link neighbor that is adjacent to the backbone.
Command Attributes
• Area ID – Identifies the transit area for the virtual link.
(The area ID must be in the form of an IPv4 address.)
•
Neighbor Router ID
– Router ID of the virtual link neighbor. This specifies the Area
Border Router (ABR) at the other end of the virtual link. To create a virtual link, it
must be configured for an ABR at both ends of the link. One of the ABRs must be
next to the isolated area and the transit area at one end of the link, while the other
ABR must be next to the transit area and backbone at the other end of the link.
(Default: None)
The other items are described under “Configuring OSPF Interfaces,” page 20-25.
20-29
CLI -
This example configures the interface parameters for VLAN 1.
Console(config)#interface vlan 1
Console(config-if)#ip ospf priority 5
Console(config-if)#ip ospf transmit-delay 6
Console(config-if)#ip ospf retransmit-interval 7
Console(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 5
Console(config-if)#ip ospf dead-interval 50
Console(config-if)#ip ospf cost 10
Console(config-if)#ip ospf authentication message-digest
Console(config-if)#ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 aiebel
Console#
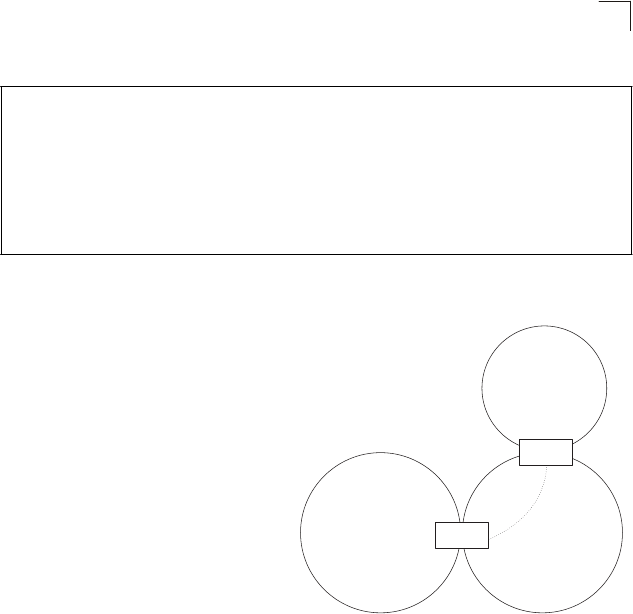
Configuring Virtual Links
A
ll OSPF areas must connect to the
backbone. If an area does not have a
direct physical connection to the
backbone, you can configure a
virtual link that provides a logical
path to the backbone. To connect an
Configuring the Open Shortest Path First Protocol
20
42-37
42-38
42-38
42-36
42-36
42-35
42-32
4
2
-
3
4
isolated
area
isolated area to the backbone, the ABR
logical path can cross a single
non-backbone area (i.e., transit area)
virtual
to reach the backbone. To define this
path, you must configure an ABR
that serves as an endpoint
connecting the isolated area to the
common transit area, and specify a
neighboring ABR as the other
backbone
link
A
BR
normal
area


















