Mapping DSCP Priority
The DSCP is six bits wide, allowing coding for up to 64 different forwarding
behaviors. The DSCP replaces the ToS bits, but it retains backward compatibility
with the three precedence bits so that non-DSCP compliant, ToS-enabled devices,
will not conflict with the DSCP mapping. Based on network policies, different kinds of
traffic can be marked for different kinds of forwarding. The DSCP default values are
defined in the following table. Note that all the DSCP values that are not specified
are mapped to CoS value 0.
Table 13-4 Mapping DSCP Priority
IP DSCP Value CoS Value
00
81
10, 12, 14, 16 2
18, 20, 22, 24 3
26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36 4
38, 40, 42 5
48 6
46, 56 7
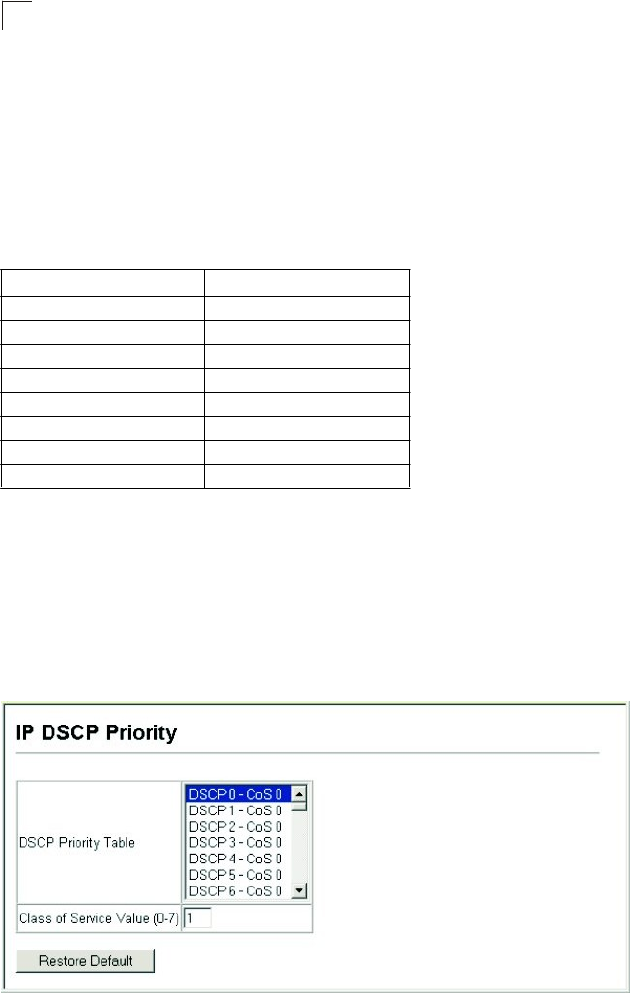
Command Attributes
• DSCP Priority Table – Shows the DSCP Priority to CoS map.
• Class of Service Value – Maps a CoS value to the selected DSCP Priority value.
Note that “0” represents low priority and “7” represent high priority.
Note: IP DSCP settings apply to all interfaces.
Web
– Click Priority, IP DSCP Priority. Select an entry from the DSCP table, enter a
value in the Class of Service Value field, then click Apply.
Figure 13-7 IP DSCP Priority
13-10
Class of Service
13


















