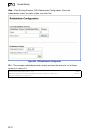
Configuring General Protocol Settings
RIP is used to specify how routers exchange routing information. When RIP is
enabled on this router, it sends RIP messages to all devices in the network every 30
seconds (by default), and updates its own routing table when RIP messages are
received from other routers. To communicate properly with other routers using RIP,
you need to specify the RIP version used globally by the router, as well as the RIP
send and receive versions used on specific interfaces (page 20-6).
Command Attributes
Global Settings
• RIP Routing Process – Enables RIP routing for all IP interfaces on the router.
(Default: Disabled)
• Global RIP Version – Specifies a RIP version used globally by the router.
(Default: RIP Version 1)
When you specify a Global RIP Version, any VLAN interface not previously set to
a specific Receive or Send Version (page 20-6) is set to the following values:
- RIP Version 1 configures previously unset interfaces to send RIPv1 compatible
protocol messages and receive either RIPv1 or RIPv2 protocol messages.
- RIP Version 2 configures previously unset interfaces to use RIPv2 for both
sending and receiving protocol messages.
RIP send/receive versions set on the RIP Interface Settings screen (page 20-6)
always take precedence over the settings for the Global RIP Version.
Timer Settings
The timers must be set to the same values for all routers in the network.
• Update – Sets the rate at which updates are sent. This is the fundamental timer
used to control all basic RIP processes. This value will also set the timeout timer
to 6 times the update time, and the garbage-collection timer to 4 times the update
time. (Range: 15-60 seconds; Default: 30 seconds)
Setting the update timer to a short interval can cause the router to spend an
excessive amount of time processing updates. On the other hand, setting it to an
excessively long time will make the routing protocol less sensitive to changes in the
network configuration.
• Timeout – Sets the time after which there have been no update messages that a
route is declared dead. The route is marked inaccessible (i.e., the metric set to
infinite) and advertised as unreachable. However, packets are still forwarded on
this route. (Default: 180 seconds)
• Garbage Collection – After the timeout interval expires, the router waits for an
interval specified by the garbage-collection timer before removing this entry from
the routing table. This timer allows neighbors to become aware of an invalid route
prior to purging. (Default: 120 seconds)
20-3
Configuring the Routing Information Protocol
20