Configuring the Open Shortest Path First Protocol
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is more suited for large area networks which
experience frequent changes in the links. It also handles subnets much better than
RIP. OSPF protocol actively tests the status of each link to its neighbors to generate
a shortest path tree, and builds a routing table based on this information. OSPF then
utilizes IP multicast to propagate routing information. A separate routing area
scheme is also used to further reduce the amount of routing traffic.
Note:
The OSPF protocol implemented in this device is based on RFC 2328 (Version 2).
It also supports RFC 1583 (early Version 2) compatibility mode to ensure that the
same method is used to calculate summary route costs throughout the network
when older OSPF routers exist; as well as the not-so-stubby area option
(RFC 3101).
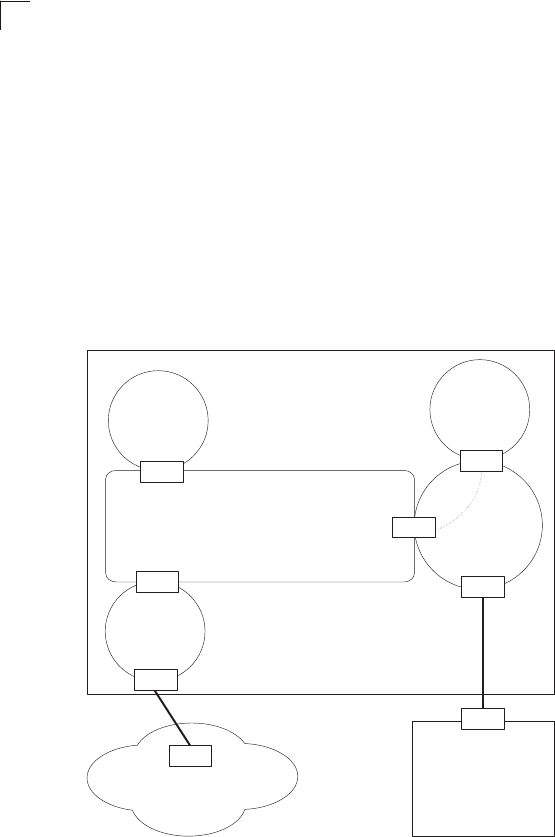
isolated
area
ABR
virtual
link
A
BR
normal
area
ASBR
ASBR
stub
ABR
ABR
NSSA
ASBR
backbone
Autonomous System A
Router
external network
Autonomous System B
Command Usage
• OSPF looks at more than just the simple hop count. When adding the shortest path
to any node into the tree, the optimal path is chosen on the basis of delay,
throughput and connectivity. OSPF utilizes IP multicast to reduce the amount of
routing traffic required when sending or receiving routing path updates. The
separate routing area scheme used by OSPF further reduces the amount of routing
traffic, and thus inherently provides another level of routing protection. In addition,
all routing protocol exchanges can be authenticated. Finally, the OSPF algorithms
have been tailored for efficient operation in TCP/IP Internets.
20-14
Unicast Routing
20