Assigning Ports to Multicast Services
Multicast filtering can be dynamically configured using IGMP Snooping and IGMP
Query messages as described in “Configuring IGMP Snooping and Query
Parameters” on page 15-3. For certain applications that require tighter control, you
may need to statically configure a multicast service on the switch. First add all the
ports attached to participating hosts to a common VLAN, and then assign the
multicast service to that VLAN group.
Command Usage
• Static multicast addresses are never aged out.
• When a multicast address is assigned to an interface in a specific VLAN, the
corresponding traffic can only be forwarded to ports within that VLAN.
Command Attribute
• Interface – Activates the Port or Trunk scroll down list.
• VLAN ID – Selects the VLAN to propagate all multicast traffic coming from the
attached multicast router/switch. (Range: 1-4093)
• Multicast IP – The IP address for a specific multicast service
• Unit – Stack unit. (Range: 1-8)
• Port or Trunk – Specifies the interface attached to a multicast router/switch.
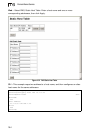
Web
– Click IGMP Snooping, IGMP Member Port Table. Specify the interface
attached to a multicast service (via an IGMP-enabled switch or multicast router),
indicate the VLAN that will propagate the multicast service, specify the multicast IP
address, and click Add. After you have completed adding ports to the member list,
click Apply.
Figure 15-5 IGMP Member Port Table
CLI – This example assigns a multicast address to VLAN 1, and then displays all the
known multicast services supported on VLAN 1.
Console(config)#ip igmp snooping vlan 1 static 224.1.1.12
ethernet 1/12
Console(config)#exit
Console#show mac-address-table multicast vlan 1
VLAN M'cast IP addr. Member ports Type
---- --------------- ------------ -------
1 224.1.1.12 Eth1/12 USER
1 224.1.2.3
E
th1/12
I
GMP
37-2
37-4
15-9
Layer 2 IGMP (Snooping and Query)
15