You can specify the IP subnets connected to this router by manually assigning an
IP address to each VLAN, or by using the RIP or OSPF dynamic routing protocols to
identify routes that lead to other interfaces by exchanging protocol messages with
other routers on the network.
Once IP interfaces have been configured, the switch functions as a multilayer
routing switch, operating at either Layer 2 or 3 as required. All IP packets are routed
directly between local interfaces, or indirectly to remote interfaces using either static
routing or dynamic routing. All other packets for non-IP protocols (for example,
NetBuei, NetWare or AppleTalk) are switched based on MAC addresses.
Command Usage
• If this router is directly connected to end node devices (or connected to end nodes
through shared media) that will be assigned to a specific subnet, then you must
create a router interface for each VLAN that will support routing. The router
interface consists of an IP address and subnet mask. This interface address
defines both the network prefix number to which the router interface is attached
and the router’s host number on that network. In other words, a router interface
address defines the network segment that is connected to that interface, and
allows you to send IP packets to or from the router.
19-5
Web -
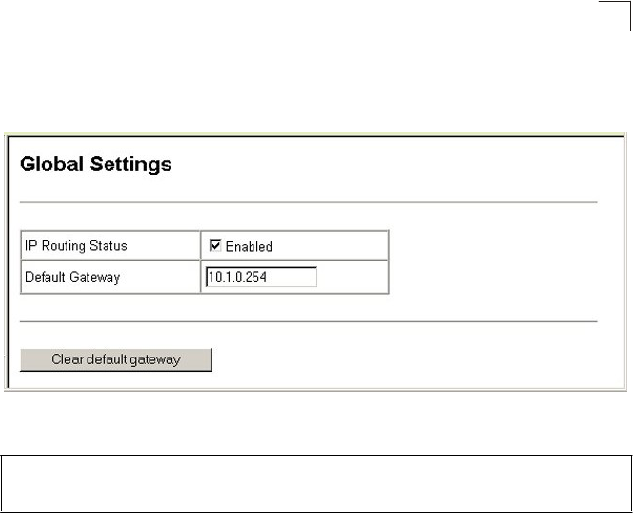
Click IP, General, Global Settings. Set IP Routing Status to Disabled to restrict
operation to Layer 2, or Enabled to allow multilayer switching, specify the default
gateway which will be forwarded packets for all unknown subnets, and click Apply.
Figure 19-1 IP Global Settings
CLI -
This example enables IP routing, and sets the default gateway.
Console(config)#ip routing
Console(config)#ip route default 10.1.0.254
Console(config)#
Configuring IP Routing Interfaces
42-1
4
2
-
2
Configuring IP Routing Interfaces
19


















