1-14
Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-9639-06
Chapter 1 Overview
Network Configuration Examples
• “Layer 2 VPN Application” section on page 1-15
• “Multi-VRF CE Application” section on page 1-16
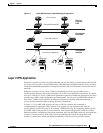
Multidwelling or Ethernet-to-the-Subscriber Network
Metro Ethernet provides the access technology for service providers deploying voice, video, and Internet
access services to metropolitan areas. The Metro Ethernet user-facing provider edge (UPE) switches
provide economical bandwidth and the security and the QoS needed for these services.
Figure 1-1 shows a Gigabit Ethernet ring for a residential location, serving multitenant units by using
Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switches connected through 1000BASE-X SFP module ports. Cisco ME
switches used as residential switches provide customers with high-speed connections to the service
provider point-of presence (POP).
Home access gateways are connected to the ME switches through UNIs or ENIs configured as 802.1Q
trunks. Because the default behavior on these ports allows no local switching between the ports, the
subscribers are protected from each other. UNIs also do not process control protocols from customers,
so denial-of-service attacks are avoided. The Cisco ME switch also provides mechanisms such as port
security and IP Source Guard to protect against MAC or IP spoofing. By using advanced access control
lists, the service providers have granular control of the types of traffic to enter the network.
To provide differential QoS treatment for different types of traffic, the Cisco ME switch can identify,
police, mark, and schedule traffic types based on Layer 2 to Layer 4 information. The Cisco modular
QoS command-line interface (CLI), or MQC, on Cisco ME switches provides an efficient method of QoS
configuration. You can configure a policer on ingress UNIs to ensure that a customer can send only the
amount of bandwidth paid for. On egress NNIs, you can use four different queues to provide different
levels of priority for different types of traffic. One queue can be assigned as a low-latency queue to
provide expedited service for latency sensitive traffic such as voice. You can also configure a rate-limiter
on the low-latency queues to prevent other queues from being deprived due to misconfiguration.
When an end station in one VLAN needs to communicate with an end station in another VLAN, a router
or switch routes the traffic to the appropriate destination VLAN, providing inter-VLAN routing. VLAN
access control lists (VLAN maps) provide intra-VLAN security and prevent unauthorized users from
accessing critical pieces of the network. The routers also provide firewall services, Network Address
Translation (NAT) services, voice-over-IP (VoIP) gateway services, and WAN and Internet access.