3300 ICP Hardware User Guide
100 Release 3.3
•Answer
• Clear Backward
• Clear Forward
• Blocking
Register Signaling
In the R2 protocol, register signaling is used during the call setup process to exchange
information about the calling and called party numbers and the calling party category. You can
use IMAT to define any of the specific tones used in R2 register signaling.
R2 register signals are defined as either forward or backward signals. Forward, or outgoing,
signals are generated by the originator of a call. Backward, or incoming, signals are generated
by the terminating end of a call. Forward and backward signals are grouped into the categories
shown in the following table.
When you are defining the specific signals in each group, the IMAT menus list each tone number
and the corresponding signal token. The following tables list the tokens in each group, and their
meanings.
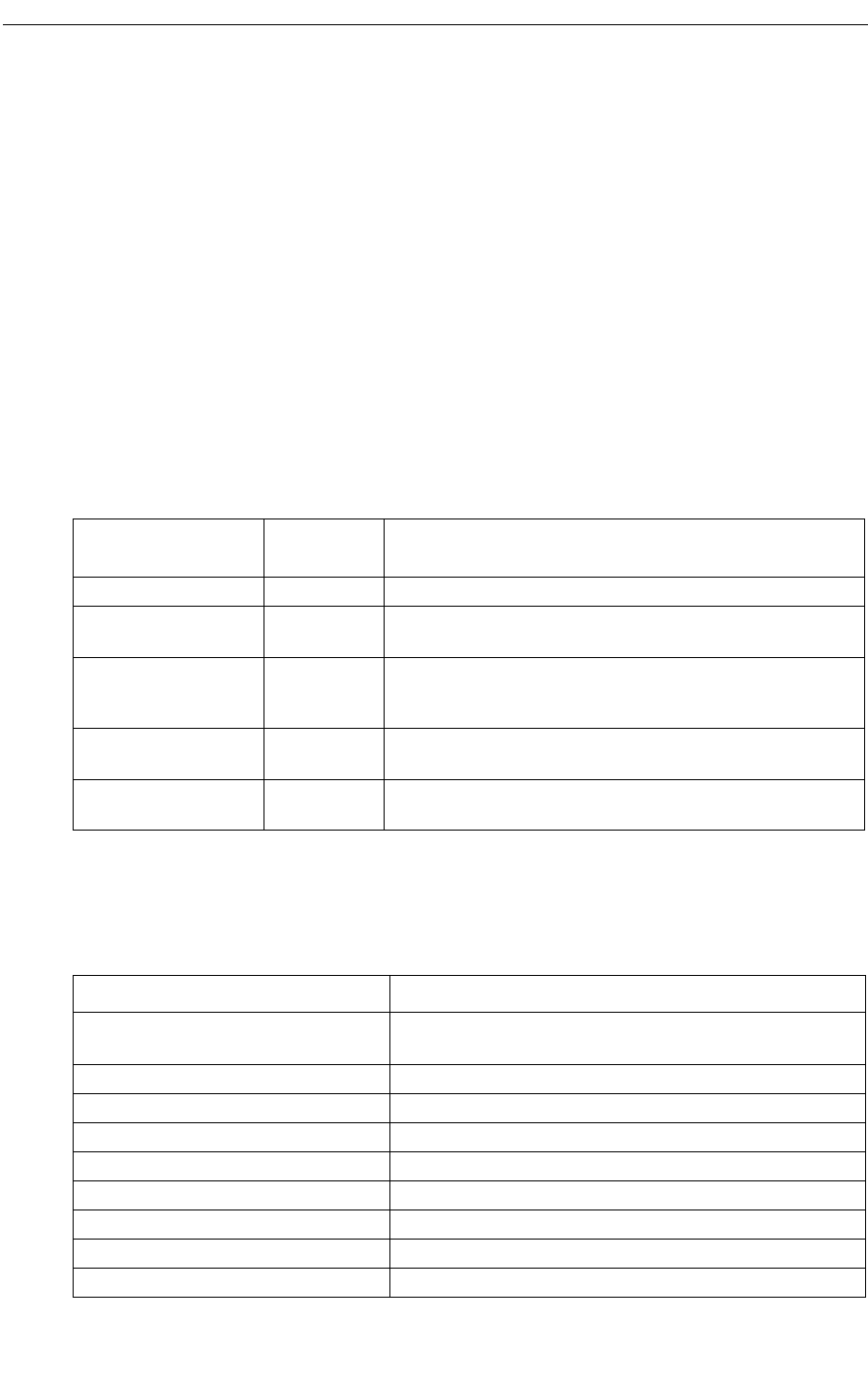
R2 Signaling
Signal direction
Event
Group
Function
Forward (outgoing) Group I Transmits digit information.
Group II Transmits the category of the calling party (such as a coin
box) and calling line identification.
Backward (incoming) Group A Acknowledges Group I signals, and requests digit
information and the category and identification of the calling
party.
Group B Acknowledges Group II signals and transmits status
information about the called party (such as busy).
Group C Acknowledges Group I signals and requests digit
information for the calling party (optional).
Event Group I
Event Token Description
T1_DIGIT_1
to T1_DIGIT_9
Process digit 1
to Process digit 9
T1_DIGIT_0 Process digit 0
T1_INCOMING_OP Marks the caller as an operator
T1_DELAY_OP Marks the caller as a delay operator
T1_ACCS_TEST_EQUIP Marks the caller as test equipment
T1_REQ_HALF_ECHO_ SUPRES Indicates that the call requires half-echo suppression
T1_END_OF_INFO Indicates end of pulsing
T1_SPARE Spare token
T1_REQ_NOT_ ACCEPTED Call setup request is not accepted