259
CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS
4
4.26 Overlap/Dead Band Function
4.26 Overlap/Dead Band Function
In heating-cooling control, the temperature process value (PV) significantly changes due to slight heating or cooling
control output when the heat produced by a controlled object and natural cooling are being balanced. Consequently,
excessive temperature output may be performed.
The temperature where the cooling control output starts can be shifted using this function; therefore, whether control
stability is prioritized or energy saving is prioritized can be selected.
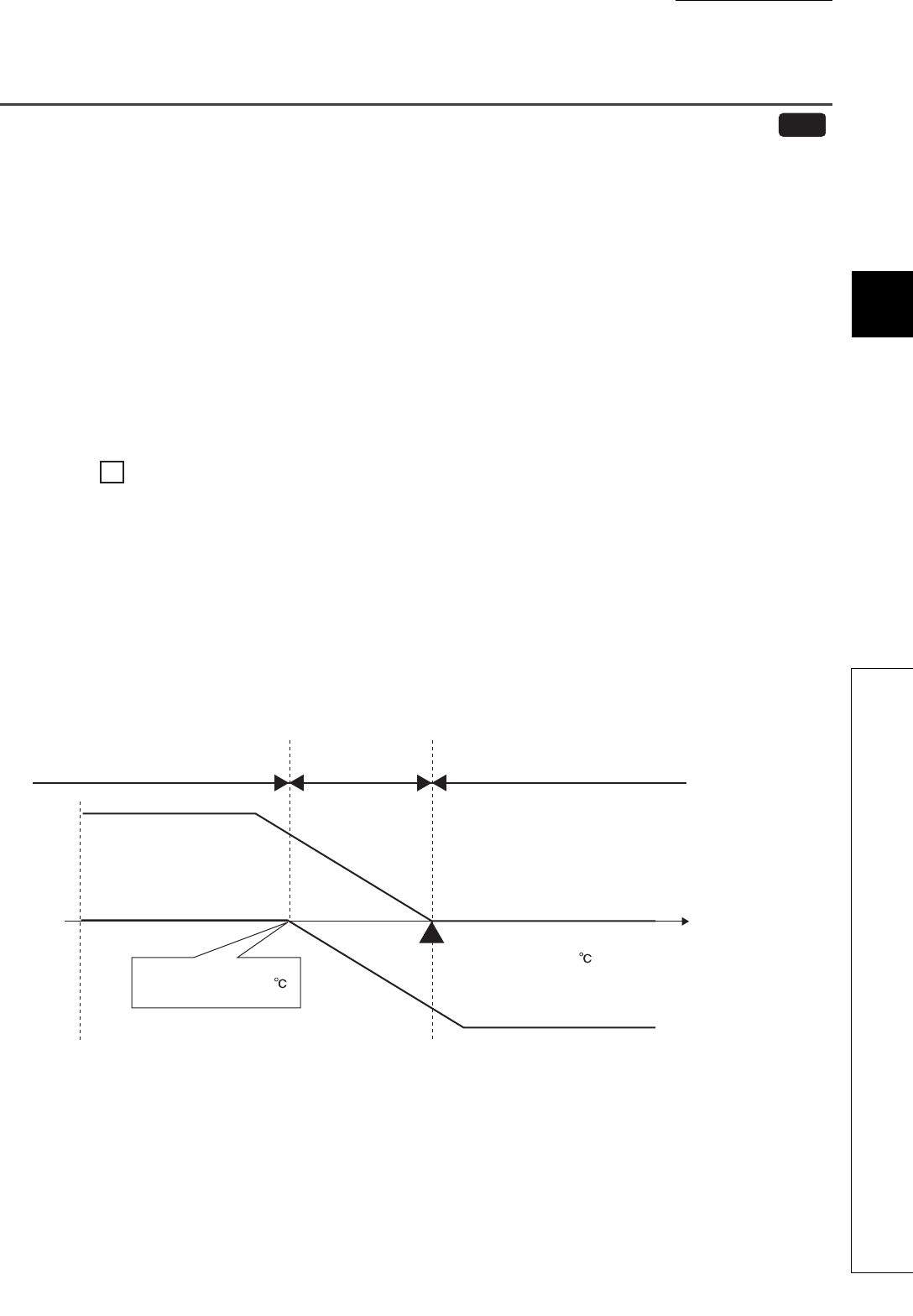
(1) Overlap
Overlap refers to the temperature area where both of heating control and cooling control are performed. In the
temperature area where both heating and cooling output overlap, both of the output negate each other, thus the
control gain becomes moderate. Consequently, the change amount in the temperature process value (PV) for the
output becomes small, improving control stability.
Ex.
When buffer memory values are set as following:
•CH Input range (Un\G32, Un\G64, Un\G96, Un\G128): 38 (temperature measurement range: -200.0°C to
400.0°C)
•CH Set value (SV) setting (Un\G34, Un\G66, Un\G98, Un\G130): 2000 (200.0°C)
•CH Overlap/dead band setting (Un\G723, Un\G739, Un\G755, Un\G771): -25 (-2.5%)
185.0°C to 200.0°C is the overlapping area.
(Full scale) × (Overlap setting) = (400.0°C - (-200.0°C)) × -0.025 = -15.0°C
The temperature where cooling operation starts = (Set value (SV)) - 15.0°C = 185.0°C
As shown below, shifting the temperature where cooling operation starts to the lower temperature side of
the set value (SV) produces an overlapping area. (The following is an example of when the module is in P
control.)
Heating-cooling
Heating only
(manipulated value for cooling (MVc): 0%)
Heating/Cooling
Cooling only
(manipulated value for heating (MVh): 0%)
Heating
Set value (SV) is 200.0 .
Cooling
Temperature
process value (PV)
Cooling starts at 185.0 .
100%
0%
-100%


















