Chapter 2
System Component Descriptions
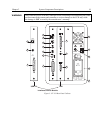
MicroMAX Camera
CCD Array: MicroMAX offers a choice of CCD technologies to improve quantum
efficiency (QE) and blue/green sensitivity. Arrays are available in full-frame, interline,
and frame-transfer formats. Thinned, back-illuminated devices have a higher QE across
the entire visible spectrum and far superior sensitivity in the blue/ green region than
front-illuminated CCDs. The MicroMAX combines back-illumination technology with
frame-transfer readout to provide high sensitivity with nonshuttered operation. Interline-
transfer CCDs contain alternate columns of imaging and storage cells.
Because the charge on each image pixel never has to transfer m
ore than one row, the
transfer can be made very quickly without smearing. By attaching microlenses to an
interline-transfer CCD, incident light is directed to the photosensitive areas of the sensor.
As a result, lens-on-chip formats dramatically improve the QE in the blue/green region of
the spectrum while still allowing fast imaging. Since no shutter is required, high-speed
gating and faster focus are possible.
CCD Chamber: The vacuum
-sealed CCD chamber protects the CCD from
contamination as well as insulates it from the warmer air in the camera body. The
inherent low humidity prevents condensation on the cooled surface of the array. The
thermal barrier provided by the vacuum isolates the window from the cooled CCD, keeps
the window from cooling below the dewpoint, and thereby prevents condensation on the
outside of the window.
MicroMAX cameras are normally shipped with a vacuum level of ~10 mTorr or better.
Because this vacuum
may deteriorate over time due to outgassing of electrical
components, round head MicroMAX cameras are designed with a built-in vacuum port
that can be used to restore the vacuum to its original level. Instructions for repumping the
vacuum are provided in Appendix C.
Window: The cam
era has one window in the optical path. The high-quality optical
quartz window is integral to the vacuum chamber. By having only one window, the
MicroMAX camera reduces the chance of image degradation due to multiple reflections,
stray light, and interference patterns that may occur with a multiple-window design.
Thermoelectric Cooler: While the CCD accum
ulates charge, thermal activity releases
electrons, generating dark current. Cooling the CCD enhances the low-light sensitivity by
reducing thermally generated charge. With forced-air assistance the MicroMAX camera’s
thermoelectric cooler is capable of cooling the CCD to -35°C with ±0.04°C stability at
temperature lock.
Cooling is accomplished by mounting the CCD on a cold finger, which in turn is seated
on a therm
oelectric (Peltier-effect) cooler, and then transferring heat through the Peltier
stages to the camera body where the heat is then radiated via a fins and removed by
15