94 MicroMAX System User Manual Version 6.C
ESABI: Allows two fast images of equal duration to be acquired. Unlike the IEC and
EEC modes, in the ESABI mode, two pulses are applied to the Ext. Sync.
connector. Each initiates a separate acquisition, allowing the user to set the time
between acquisitions by externally adjusting the time between the two applied pulses.
When the data is saved, both images are saved in a single *.spe file. The header is
followed by
frame 1 and then immediately afterwards by frame 2. This system m
akes it
t to later load the im
ages from the file for post-processing analysis. convenien
Notes:
1. ra tab page (Hardware on the Setup The Readout Mode set on the Controller/Came
menu) must be set to DIF for DIF operation.
2. SABI timing mode, set the Number of Images to 2 and In the IEC, EEC or E
Accumulations to 1.
3. ry Values button. On the Setup Hardware Cleans/Skips tab page, click the Load Facto
This step is necessary for proper operation of the interline camera.
4. For most of the MicroMAX DIF cameras, the ESABI timing mode is activated and
deactivated via the application software. If a MicroMAX DIF camera has a switch on
its back panel, this switch must be set to the ACTIVE position for operation in the
ESABI timing mode. At all other times it must be set to INACTIVE.
Timing Mo
ing page
are ndard systems. The provided timing modes are:
e Between Images (two shot)
A discussion of each mode follows.
over long before the shutter closes.
des
The timing mode selections provided on the Acquisition Experiment Setup Tim
different from those in sta
FREERUN (single shot)
IEC: Internal Exposure Control (two shot)
EEC: External Exposure Control (two shot)
ESABI: Electronic Shutter Activ
Free Run
The Free Run mode allows the user to capture single images. The exposure time is set on
the Experiment Setup Main tab page, the same as in non-DIF systems, with the
difference that the exposure time can be as short as one 1 µs (maximum exposure time is
14.3 minutes). It often proves convenient to simply disable the mechanical shutter open
in Free Run operation. The shutter requires ~8 ms to open and 8 ms to close. The camera
waits until the shutter is completely open before acquiring the image, and in a typical
experiment, the second image acquisition will be
Readout doesn’t occur until the shutter closes.
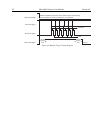
The
signal output of the controller can be used to trigger external equipment,
such as the laser. As soon as the shutter is completely opened and all of the cleans have
been performed,
goes low to indicate that th era is ready to capture an
image. As soon as the first exposure actually be
e cam
gins,
returns high, as shown in
Figure 49. Thus the positive going edge of the
output marks the start of the first