Clock Module
MCF52211 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-21
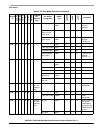
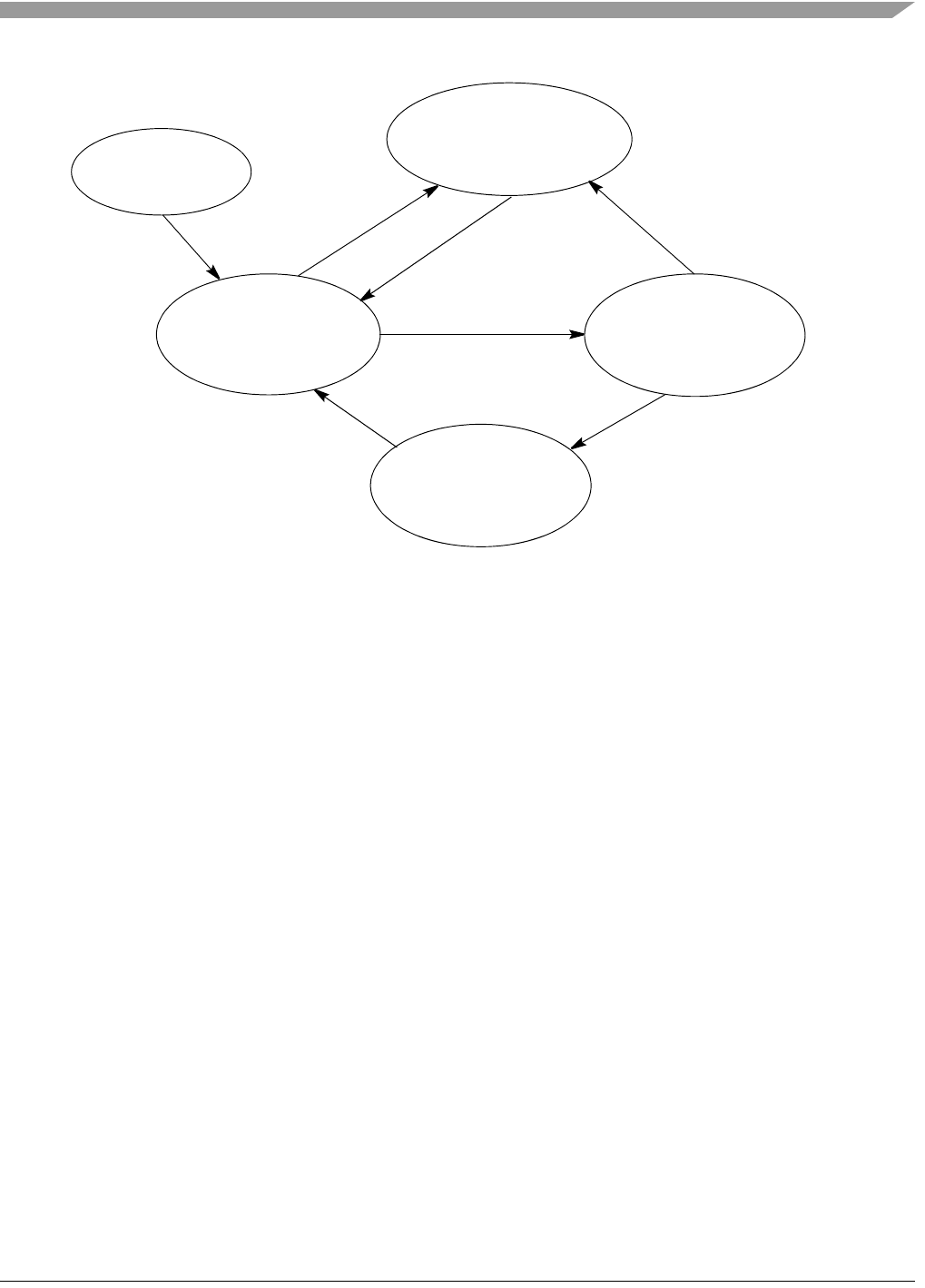
Figure 6-13. Lock Detect Sequence
6.8.4.6 PLL Loss of Lock Conditions
After the PLL acquires lock after reset, the LOCK and LOCKS flags are set. If the MFD is changed, or if
an unexpected loss of lock condition occurs, the LOCK and LOCKS flags are negated. While the PLL is
in the non-locked condition, the system clocks continue to be sourced from the PLL as the PLL attempts
to relock. Consequently, during the relocking process, the system clocks frequency is not well defined and
may exceed the maximum system frequency, violating the system clock timing specifications.
However, after the PLL has relocked, the LOCK flag is set. The LOCKS flag remains cleared if the loss
of lock was unexpected. The LOCKS flag is set when the loss of lock is caused by changing MFD. If the
PLL is intentionally disabled during stop mode, then after exit from stop mode, the LOCKS flag reflects
the value prior to entering stop mode after lock is regained.
6.8.4.7 PLL Loss of Lock Reset
If the LOLRE bit in the SYNCR is set, a loss of lock condition asserts reset. Reset reinitializes the LOCK
and LOCKS flags. Therefore, software must read the LOL bit in the reset status register (RSR) to
determine if a loss of lock caused the reset. See Section 10.5.2, “Reset Status Register (RSR).”
To exit reset in PLL mode, the reference must be present, and the PLL must achieve lock.
In external clock mode, the PLL cannot lock. Therefore, a loss of lock condition cannot occur, and the
LOLRE bit has no effect.
Count N
Reference Cycles
and Compare
Number of Feedback
Cycles Elapsed
Start
with Tight Lock
Criteria
≠ Feedback Count
Loss of Lock Detected
Set Tight Lock Criteria
and Notify System of Loss
of Lock Condition
Count N + K
Reference Cycles
and Compare Number
of Feedback Cycles
Elapsed
Lock Detected.
Set Relaxed Lock
Condition and Notify
System of Lock
Condition
Reference Count
Reference Count =
Feedback Count = N
In Same Count/Compare Sequence
Reference Count = Feedback Count = N + K
In Same Count/Compare Sequence
Reference Count
≠ Feedback Count