Interrupt Controller Module
MCF52211 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 14-7
14.3.2 Interrupt Mask Register (IMRHn, IMRLn)
The IMRHn and IMRLn registers are each 32 bits and provide a bit map for each interrupt to allow the
request to be disabled (1 = disable the request, 0 = enable the request). The IMRn is set to all ones by reset,
disabling all interrupt requests. The IMRn can be read and written. A write that sets bit 0 of the IMR forces
the other 63 bits to be set, disabling all interrupt sources, and providing a global mask-all capability.
Table 14-4. IPRLn Field Descriptions
Field Description
31–1
INT
Interrupt Pending. Each bit corresponds to an interrupt source. The corresponding IMRLn bit determines whether an
interrupt condition can generate an interrupt. At every system clock, the IPRLn samples the signal generated by the
interrupting source. The corresponding IPRLn bit reflects the state of the interrupt signal even if the corresponding
IMRLn bit is set.
0 The corresponding interrupt source does not have an interrupt pending
1 The corresponding interrupt source has an interrupt pending
0 Reserved, should be cleared.
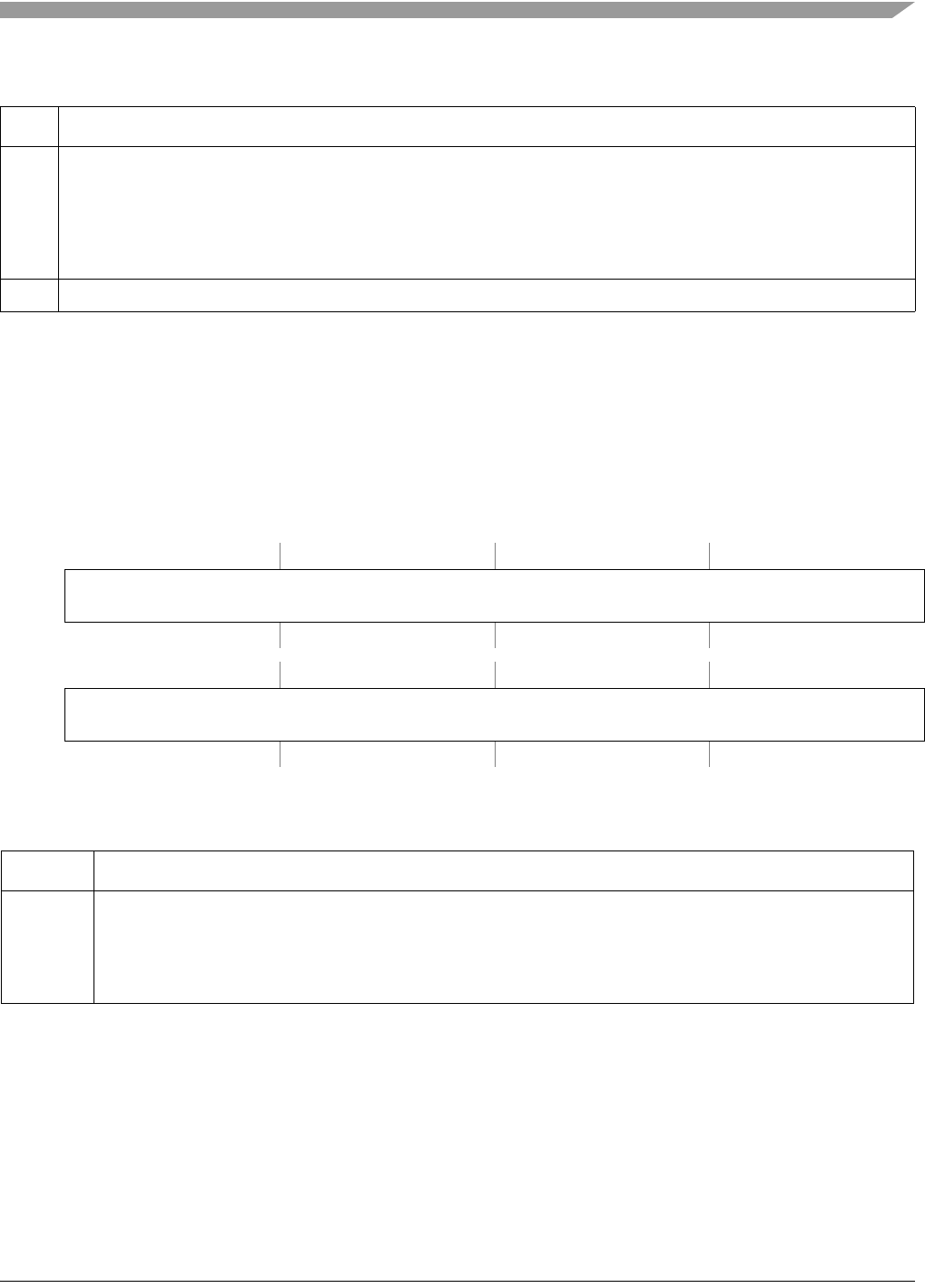
IPSBAR
Offset: 0x0C08 (IMRHn)
Access: Read/write
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
R
INT_MASK[63:48]
W
Reset1111111111111111
1514131211109876543210
R
INT_MASK[47:32]
W
Reset1111111111111111
Figure 14-3. Interrupt Mask Register High (IMRHn)
Table 14-5. IMRHn Field Descriptions
Field Description
31–0
INT_MASK
Interrupt mask. Each bit corresponds to an interrupt source. The corresponding IMRHn bit determines whether an
interrupt condition can generate an interrupt. The corresponding IPRHn bit reflects the state of the interrupt signal
even if the corresponding IMRHn bit is set.
0 The corresponding interrupt source is not masked
1 The corresponding interrupt source is masked


















