Chapter 1
Overview
Backplane (Fabric)
38
The HSO connects to the system backplane through an HMZD2X10 right-angle receptacle.
sx2000 RCS Module
The sx2000 RCS module supplies clocks to the Superdome sx2000 backplane, communicates clock alarm to
the RPM, and accepts control input from the RPM. It has an I2C EEPROM on the module so that the the
firmware can inventory the module on system power up.
The RCS supplies 16 copies of the sine wave system clock to the sx2000 system backplane. Eight copies go to
the eight cell boards, six copies to the six XBCs on the system backplane, and two copies to the backplane
clock power detector.
In normal operation the RCS selects one of the two HSOs as the source of clocks for the platform. Which HSO
is selected depends whether the HSO is plugged into the backplane and on whether it has a valid output level.
This selection is overridden if there is a connection from the clock input MCX connector on the master
backplane. Figure 1-5 shows the locations of the HSOs and RCS on the backplane.
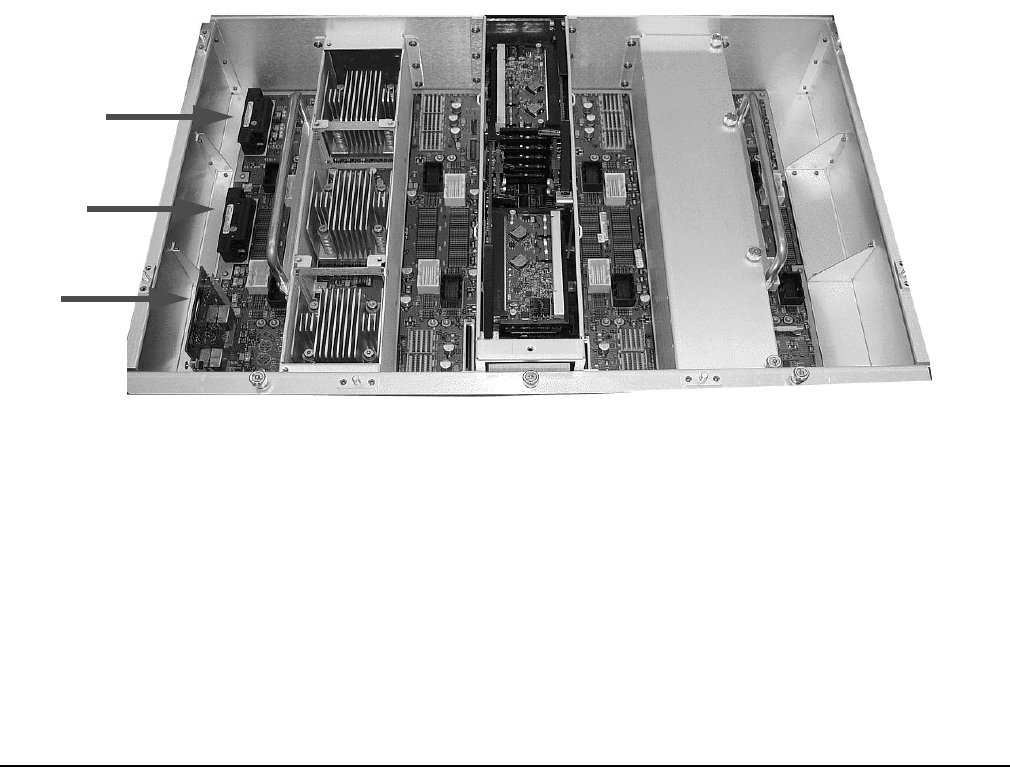
Figure 1-5 Locations of HSO and RCS
If only one HSO is plugged in and its output is of valid amplitude then it is selected. If its output is valid, then
a green LED on the HSO is lit. If its output is not valid, then a yellow LED on the HSO is lit and an alarm
signal is sent from the RCS to the RPM. The RCS provides a clock that is approximately 100 KHZ less than
the correct frequency even if the output of the HSOs are not of valid amplitude or no HSOs plugged in.
If both HSOs are plugged in and their output amplitudes are valid, then one of the two is selected as the clock
source by logic on the RCS. The green LEDs on both HSOs will be lit.
HSO 0
HSO 1
RCS


















