Appendix B • The Internet and the DW4020
72
1031484-0001 Revision 2
their TCP limits, vastly increasing the overall throughput. This
technique is also known as TCP spoofing.
IP addressing and the
DW4020
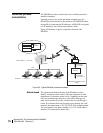
IP provides a method of constructing a network of networks
where computers and networks made by different manufacturers
and conforming to different standards can exchange information.
The IP is layered on top of vendor-specific protocols. The data to
be sent is divided into packets. IP directs each packet based on a
four-byte destination address, the IP address, in the IP packet
header.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns ranges
of IP addresses to Internet Service Providers (ISPs), who assign
ranges to organizations, who are their customers. The
organizations, in turn, assign individual numbers within that
range to each of their networked computers.
In this way, every computer on a network, (each computer on a
network may also be referred to as a "host") is assigned a unique
number that identifies it and its network. Actually, the IP address
is assigned to the connection rather than to the computer itself.
However, it is assumed that the computers are not moved from
their respective connections. By convention, these IP addresses
are written by converting each byte (8 bits) into a decimal number
(0 to 255) and separating each byte by a period as in 192.77.43.4.
This format, called dotted decimal notation, is used to enter IP
addresses.
It is important to note that IANA defines an "enterprise" as an
entity autonomously operating a network using TCP/IP and in
particular determining the addressing plan and address
assignments within that network. Thus, in the context of TCP/IP,
installing networks or DW4020s, or assigning IP addresses, the
term enterprise refers to an organization defined in this way.
As an example of Internet address assignment, a small business
owner with four networked computers might apply to IANA or its
ISP for a “class C” network. In the IP address for a class C
network the first three bytes identify the network and the last byte
identifies the individual computer. The business owner is
assigned the numbers 192.77.43.*, where * represents a “wild