Appendix B • The Internet and the DW4020
74
1031484-0001 Revision 2
Private IP addresses
As Internet use has increased, more and more IP addresses have
been assigned. There is not an infinite number of IP addresses,
and IANA is concerned that the supply of unique IP addresses
could be exhausted. One way to conserve IP addresses is to assign
them only to hosts that are designated as "public." Hosts that are
designated as "private" do not need unique IP addresses.
Types of hosts
IANA has created three categories of hosts:
Category 1: hosts that do not require access to hosts in other
enterprises or the Internet at large; hosts within this category
may use IP addresses that are unambiguous within an
enterprise, but may be ambiguous between enterprises.
Category 2: hosts that need access to a limited set of outside
services (e.g., E-mail, FTP, netnews, remote login) which can
be handled by mediating gateways (e.g., application layer
gateways). For many hosts in this category an unrestricted
external access (provided via IP connectivity) may be
unnecessary and even undesirable for privacy/security
reasons. Just like hosts within the first category, such hosts
may use IP addresses that are unambiguous within an
enterprise, but may be ambiguous between enterprises.
Category 3: hosts that need network layer access outside the
enterprise (provided via IP connectivity); hosts in the last
category require IP addresses that are globally unambiguous.
Hosts in categories 1 and 2 are private hosts. Hosts in Category 3
are public hosts. Hosts in categories 1 and 2 do not need to be
directly accessible from other networks. These hosts might
include airport arrival/departure displays, automatic teller
machines, or equipment at clerical positions. Thus, these private
hosts do not need unique IP address numbers. The IP addresses
private hosts are assigned need only be unique within the
network; they need not be directly accessible from other
networks.
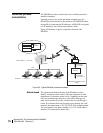
In addition, for security reasons, many enterprises use application
layer gateways to connect their internal network to the Internet.
The internal network usually does not have direct access to the
Internet; thus, only one or more gateways are visible from the
Internet. In this case, the internal network can use non-unique IP
network numbers.
In short, there are many devices that can be connected on an
internal Internet or intranet that need never be assigned unique IP
addresses. In this way, IP addresses are conserved.
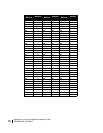
Private address space
IANA has reserved the following three blocks of the IP address
space for private internets: