Appendix B • The Internet and the DW4020
1031484-0001 Revision 2
73
card.” The business owner can then assign his individual
computer connections the numbers as shown in Figure 51.
A large organization like a university might apply for a class B
network, in which the first two bytes are assigned and the last two
bytes are available to the university to assign up to 64 thousand
computers in sub-network LANs. For example, the university
might be assigned a number like 170.15.*.*. The university, in
turn, could make assignments such as: 170.15.100.* = Physics
department LAN sub-network, 170.15.101.* = central library
LAN1 sub-network, and so on. It is a common practice to assign
the third byte to individual department LANs and the fourth byte
to individual computers within each department.
A very large entity might require a class A network that would
allow over 16 million individual IP address assignments. Table 11
gives the ranges of IP addresses IANA reserves for specific
purposes.
HNS customers have already acquired IP address ranges and
supply these as needed to HNS installers.
Note, however, that many organizations of various sizes now use
private IP addressing (see Private IP addresses below). These
organizations do not need to assign a unique public IP address to
each computer (or "host") on their networks.
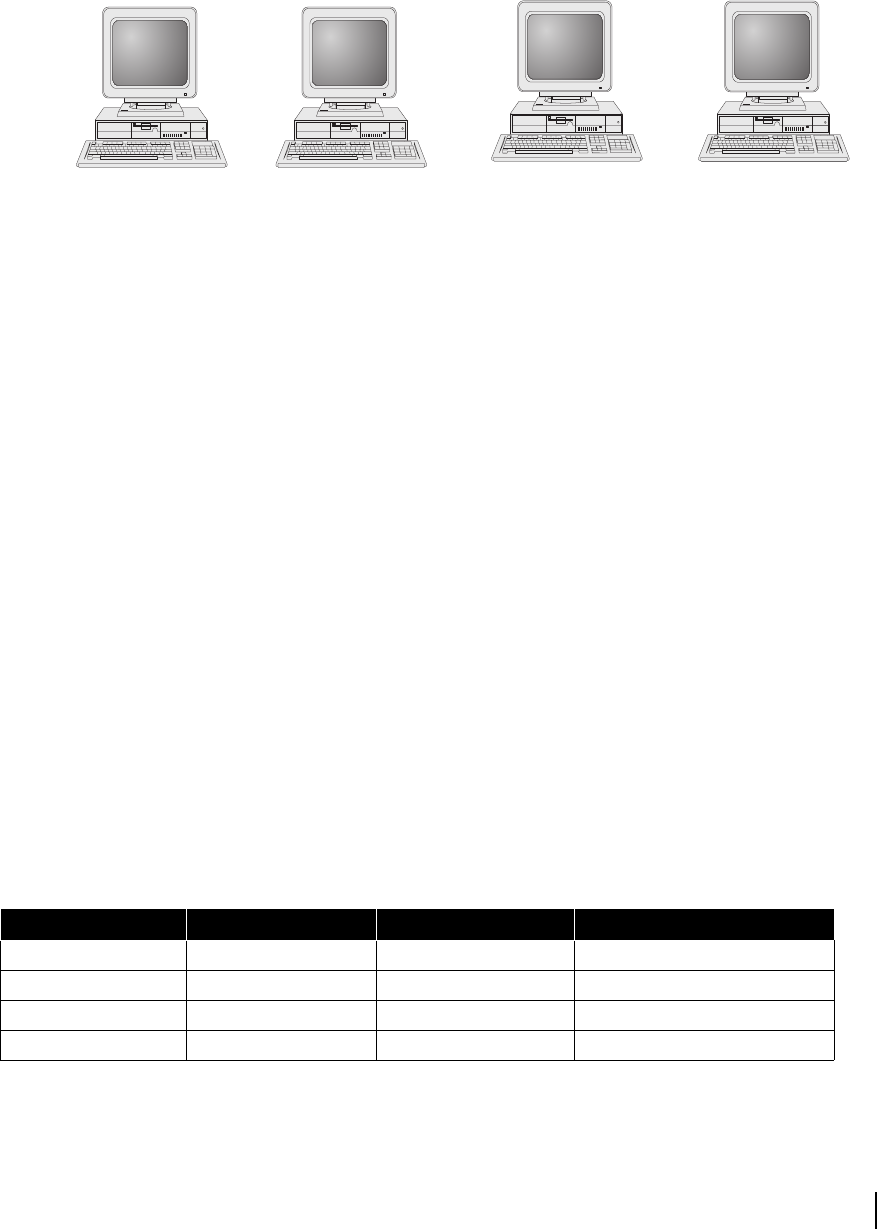
Figure 51: IP addresses assigned to individual computer connections
Internet
address
192.77.43.2 192.77.43.3
192.77.43.4 192.77.43.5
Table 11: IP Address ranges
Category Lowest address Highest address Example or comment
Class A network 0.1.0.0 126.0.0.0 9.*.*.* for IBM Corp.
Class B network 128.0.0.0 191.255.0.0 170.15.*.* – a university
Class C network 192.0.1.0 223.255.0.0 192.77.43.* – small business
D – multicast 224.0.0.0 239.255.255.255