34
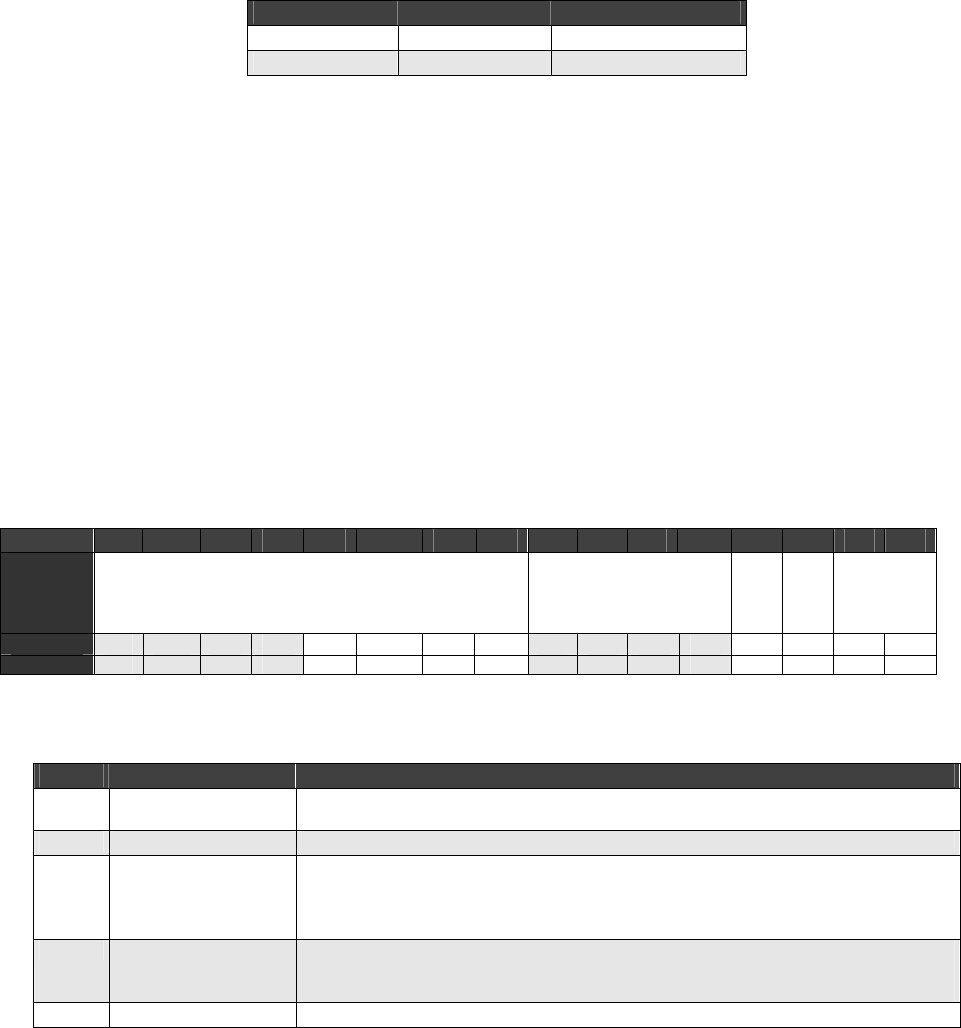
Table 4-1. USB Data Direction
Rx Tx
Device OUT or SETUP IN
Host IN OUT or SETUP
Addressing BDT Entries
Before describing how to access endpoint data via the USB or microprocessor, it is important to
understand the BDT addressing mechanism. The BDT occupies up to 256 bytes of system
memory. Sixteen bidirectional endpoints can be supported with a full BDT of 256 bytes. Eight
bytes are needed for each USB endpoint direction. Applications with less than 16 endpoints
require less Random Access Memory (RAM) to implement the BDT.
The BDT Page register points to the starting location of the BDT. The BDT must reside on a
256-byte boundary in system memory. All enabled TX and RX endpoint BD entries are indexed
into the BDT for easy access via the USB or microprocessor.
When the USB receives a USB token on an enabled endpoint, it uses its integrated DMA
controller to interrogate the BDT. The USB reads the corresponding endpoint BD entry to
determine if it owns the BD and corresponding buffer in system memory. To compute the entry
point in to the BDT, the BDT_PAGE register is concatenated with the current endpoint and the
TX and ODD fields to form the following 16- bit address.
Table 4-2. 16-Bit USB Address
BIT
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FIELD
BDT_PAGE REGISTER END_POINT
TX
ODD
///
RESET
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
RW RW RW R RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Table 4-3. 16-Bit USB Address Definitions
Bits Field Name Description
15:8 BDT_PAGE
REGISTER
Register in the Control Block
7:4 END_POINT
Endpoint Field from the USB Token
3 TX
Transmit
Shows whether the USB core is transmitting or receiving data.
1 = USB core is transmitting data.
0 = USB core is receiving data.
2 ODD
Bit That the USB SIE Maintains
This bit corresponds to the buffer currently in use. Buffers are used in a ping-pong
fashion.
1:0 ///
Reserved
Buffer Descriptor Formats
Buffer Descriptors (BDs) provide endpoint buffer control information for the USB and
microprocessor. BDs have different meanings based on which unit is reading the descriptor in
memory.
The USB controller and microprocessor use the data stored in the BDs to determine the items in
Table 4-4.


















