37
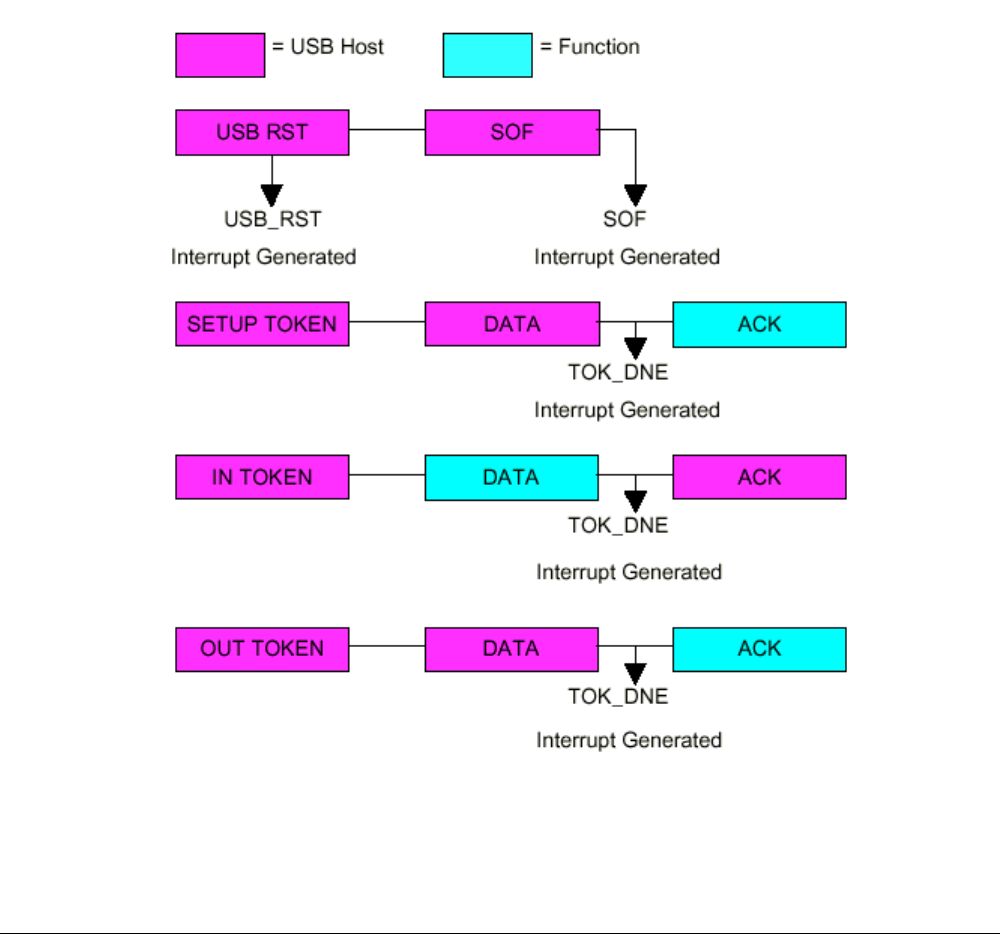
USB Transaction
When the USB transmits or receives data:
1. The USB uses the address generation in Table 4-5 to compute the BDT address.
2. After reading the BDT, if the OWN bit equals 1, the SIE DMAs the data to or from the buffer
indicated by the BD’s ADDR field.
3. When the TOKEN is complete, the USB updates the BDT and changes the OWN bit to 0 if
KEEP is 0.
4. The USB updates the STAT register and sets the TOK_DNE interrupt.
5. When the microprocessor processes the TOK_DNE interrupt:
6. The microprocessor reads the status register for the information it needs to process the
endpoint
7. The microprocessor allocates a new BD, so the endpoint can transmit or receive additional
USB data, then processes the last BD.
Figure 4-2 shows a time line for processing a typical USB token.
Figure 4-2. USB Token Transaction


















