32 www.xilinx.com Ethernet AVB Endpoint User Guide
UG492 July 23, 2010
Chapter 3: Overview of Ethernet Audio Video Bridging
P802.1Qat
This specification defines a Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP) which must be used over
the AVB network. Every listener that intends to receive audio/video AV traffic from a
talker must make a request to reserve that bandwidth. Both the talker and every bridge
device that exists between the talker and the listener has the right to decline this request.
Only if each device is capable of routing the new AV traffic stream without violating the
75% total bandwidth restriction (when taking into account previously granted bandwidth
commitments), will the bandwidth request be successful. However, after granted, this
audio / video stream is reliably routed across the network until the reservation is
removed.
Note:
No hardware components are required for the P802.1Qat specification because this is a pure
software task. This software is not provided by the Ethernet AVB Endpoint core.
Typical Implementation
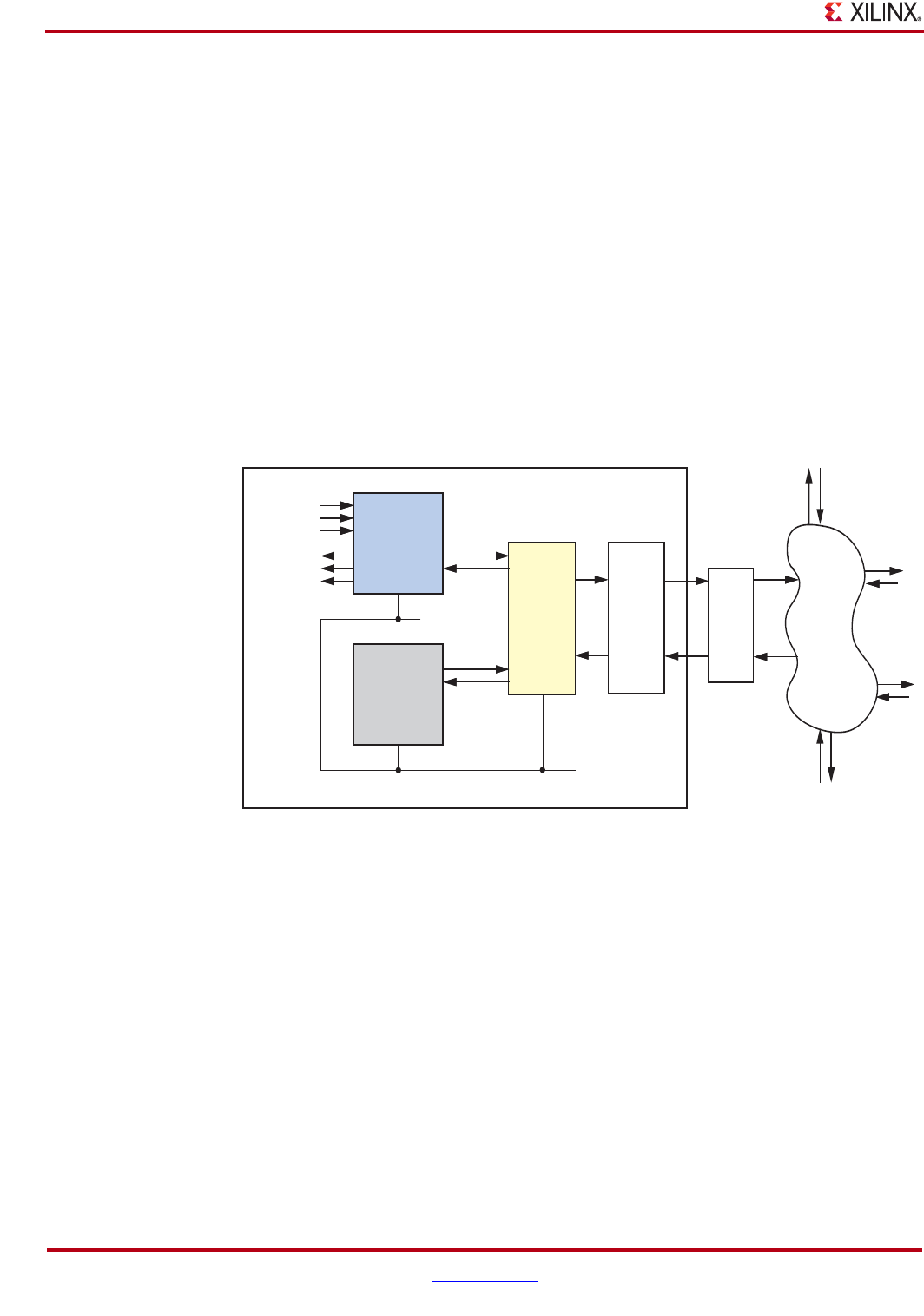
Figure 3-2 illustrates a typical implementation for the Ethernet AVB Endpoint core.
Endpoint refers to a talker or listener device from the example network shown in
Figure 3-1, as opposed to an intermediate bridge function, which is not supported.
In the implementation, the Ethernet AVB Endpoint core is shown connected to a Xilinx Tri-
Mode Ethernet MAC core, which in turn is connected to an AVB capable network. All
devices attached to this network should be AVB capable to obtain the full Quality of
Service advantages for the AV traffic. This AVB network can be a professional or consumer
network (as illustrated in Figure 3-1).
X-Ref Target - Figure 3-2
Figure 3-2: Example Ethernet AVB Endpoint System
Xilinx Device
Tri-Mode
Ethernet
MAC
LogiCORE
Ethernet
AVB
Endpoint
LogiCORE
legacy
traffic
Embedded
Processor
System
with TCP/IP
stack
AV
traffic
IEEE 1722
Packet
Manager
AVB
network
Audio /
Video
Sources /
Sinks
PLB management
Ethernet
PHY


















