106
CHAPTER 2 DEPENDENCE FUNCTIONS
2.2.8.1 Single Trace
The single trace traces all data from the start of executing a program until the program is
aborted.
■ Function of Single Trace
The single trace is enabled by setting the event mode to normal mode using the SET MODE command.
The single trace traces all data from the start of executing a program until the program is suspended.
If the real-time trace function is enabled, data sampling continues execution to record the data in the trace
buffer while the GO, STEP, CALL commands are being executed.
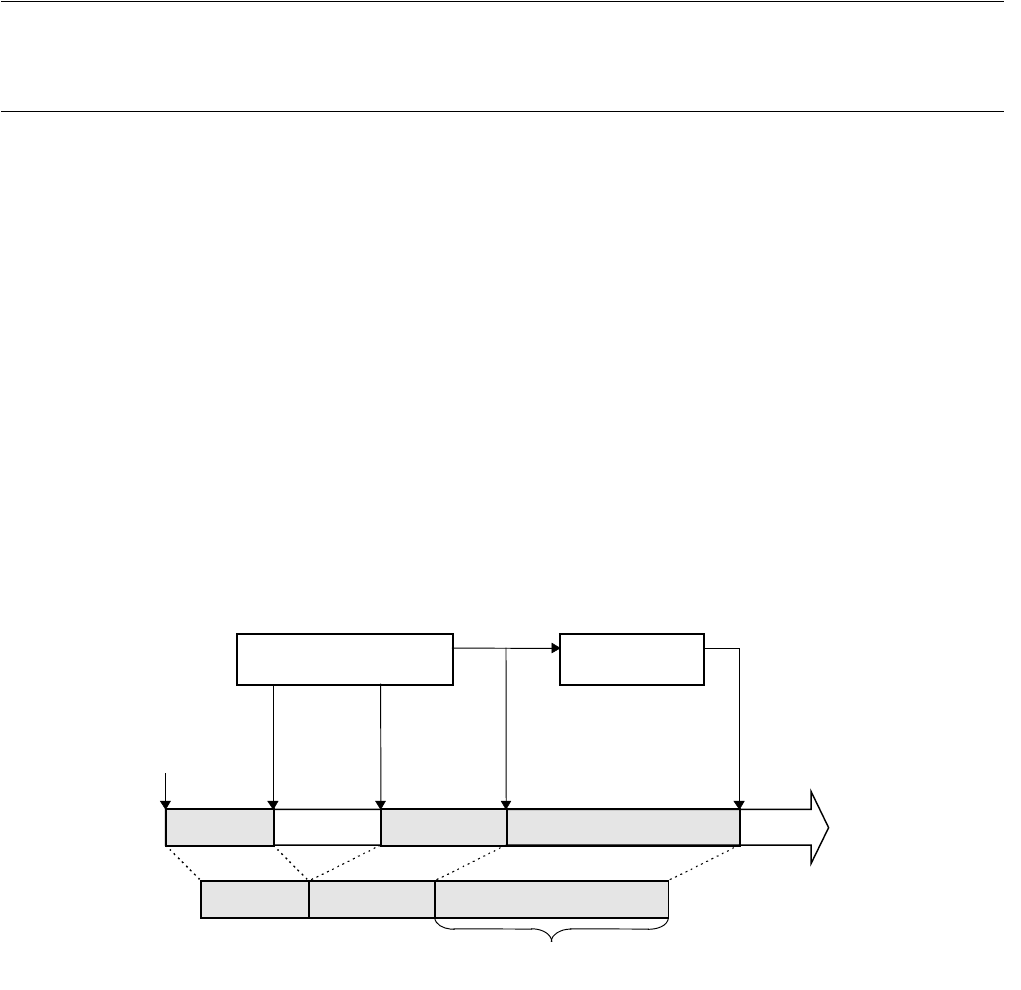
As shown in Figure 2.2-10, suspend/resume trace sampling can be controlled by the event sequencer. Since
the delay can be set between the sequencer terminating the trigger and the end of tracing, the program flow
after an given event occurrence can be traced. The delay count is counted in pass cycle units, so it matches
the sampled trace data count. However, nothing can be sampled during the delay count if trace sampling is
suspended when the sequencer is terminated.
After the delay count ends, a break occurs normally due to the sequential break, but tracing can be terminated
without a break.
Furthermore, a program can be allowed to break when the trace buffer becomes full. This break is called a
trace-buffer-full break.
Figure 2.2-10 Sampling in Single Trace
Suspend
sampling
Start program
Program flow
Trace buffer
Delay
Sequencer
Delay counter
Resume
sampling
Sequencer terminates
Trigger
Tracing
terminates


















