71
CHAPTER 2 DEPENDENCE FUNCTIONS
2.2.1.4 Memory Mapping
Memory space can be allocated to the user memory, the emulation memory, etc., and the
attributes of these areas can be specified.
However, the MCU internal resources are not dependent on this mapping setup and
access is always made to the internal resources.
■ Access Attributes for Memory Areas
The access attributes shown in Table 2.2-2 can be specified for memory areas.
A guarded memory access break occurs if access is attempted in violation of these attributes while executing
a program.
When access to the user memory area and the emulation memory area is made using program commands,
such access is allowed regardless of the CODE, READ, WRITE attributes. However, access to memory with
the GUARD attribute in the undefined area, causes an error.
When access is made to an area without the WRITE attribute by executing a program, a guarded access break
occurs after the data has been rewritten if the access target is the user memory. However, if the access target
is the emulation memory, the break occurs before rewriting. In other words, write-protection (memory data
cannot be overwritten by writing) can be set for the emulation memory area by not specifying the WRITE
attribute for the area.
This write-protection is only enabled for access made by executing a program, and is not applicable to access
by commands.
■ Creating and Viewing Memory Map
Use the following commands for memory mapping.
SET MAP: Set memory map.
SHOW MAP: Display memory map.
CANCEL MAP: Change memory map setting to undefined.
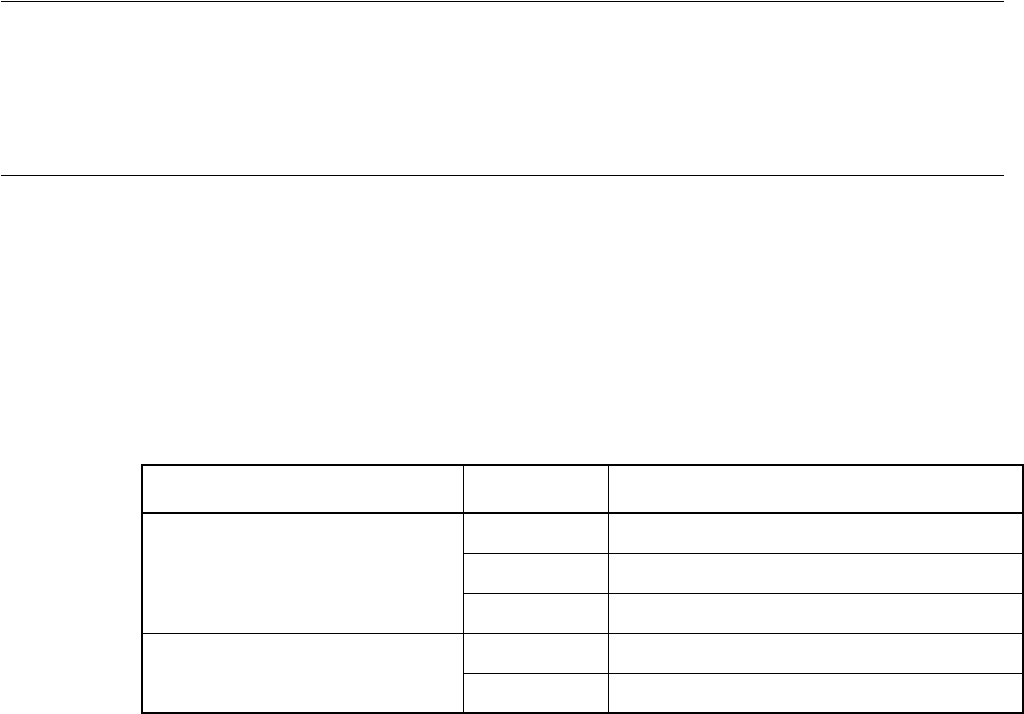
Table 2.2-2 Types of Access Attributes
Area Attribute Description
User Memory
Emulation Memory
CODE Instruction Execution Enabled
READ Data Read Enabled
WRITE Data Write Enabled
Undefined GUARD Access Disabled
NOGUARD No check of access attribute


















