Variables 427
22
Variables
Variables are placeholders for objects (such as function
definitions, numbers, matrices, the results of calculations,
and the like). Some are built-in and cannot be deleted. But
you can also create your own.
Many built-in variables are automatically assigned objects
as a result of some operation (such as defining a polar
function, performing a calculation, or setting an option).
For example, if you define a polar function, that definition
is assigned to variable named R
0
to R
n
. If you use the
Function app to find the slope of a curve at some x-value,
the slope is assigned to a variable named Slope. And if
you choose binary as the base for integer arithmetic, a
built-in variable named Base is given the value 0. If you
had chosen octal instead, Base would have been given
the value 1.
Creating variables Variables you create are assigned whatever value you
give them. You can assign a value to certain built-in
variables (such as the Home variables). You can also
create your own variables. Example 1 below gives an
example of assigning a value to a built-in variable, and
example 2 illustrates how to create a variable and assign
a value to it
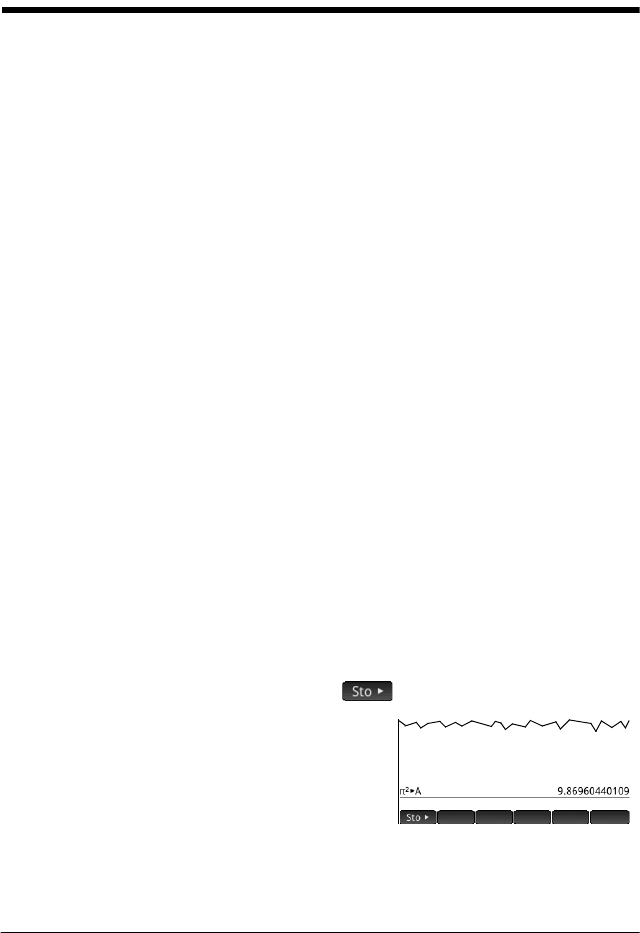
Example 1: To assign
2
to the built-in variable A:
Szj AaE
Your stored value
appears as shown at the
right. If you then wanted
to multiply your stored
value by 5, you could
enter:
Aas5E


















