Chapter 4 Explanation of Functions
4.2.91 Deceleration and stopping at power failure (nonstop deceleration at instantaneous
power failure)
You can select three modes with controller deceleration
and stop on power loss (b050).
Data or range of data Description
The nonstop deceleration at instantaneous power failure is
the function making the inverter decelerate and stop the
motor while maintaining the voltage below the overvoltage
level when an instantaneous power failure occurs during
the inverter operation.
4 - 83
Item Function code
00
Disabling the nonstop
deceleration function
01
Enabling the nonstop
deceleration function
02
Controller deceleration and stop on power loss b050
03
DC bus voltage trigger level during power loss b051 0.0 to 1000. (V)
Over-voltage threshold during power loss (*1) b052 0.0 to 1000. (V)
Deceleration time setting during power loss b053 0.01 to 3600. (s)
Initial output frequency decrease during power loss b054 0.00 to 10.00 (Hz)
Proportional gain setting for nonstop operation at
momentary power failure
b055 0.00 to 2.55
Proportional gain at DC voltage
constant control(Only when
"02" or "03" is specified for
b050)
Integral time setting for nonstop operation at
momentary power failure
b056
0.0 to 9.999 /
10.00 to 65.53
Integral time at DC voltage
constant control(Only when
"02" or "03" is specified for
b050)
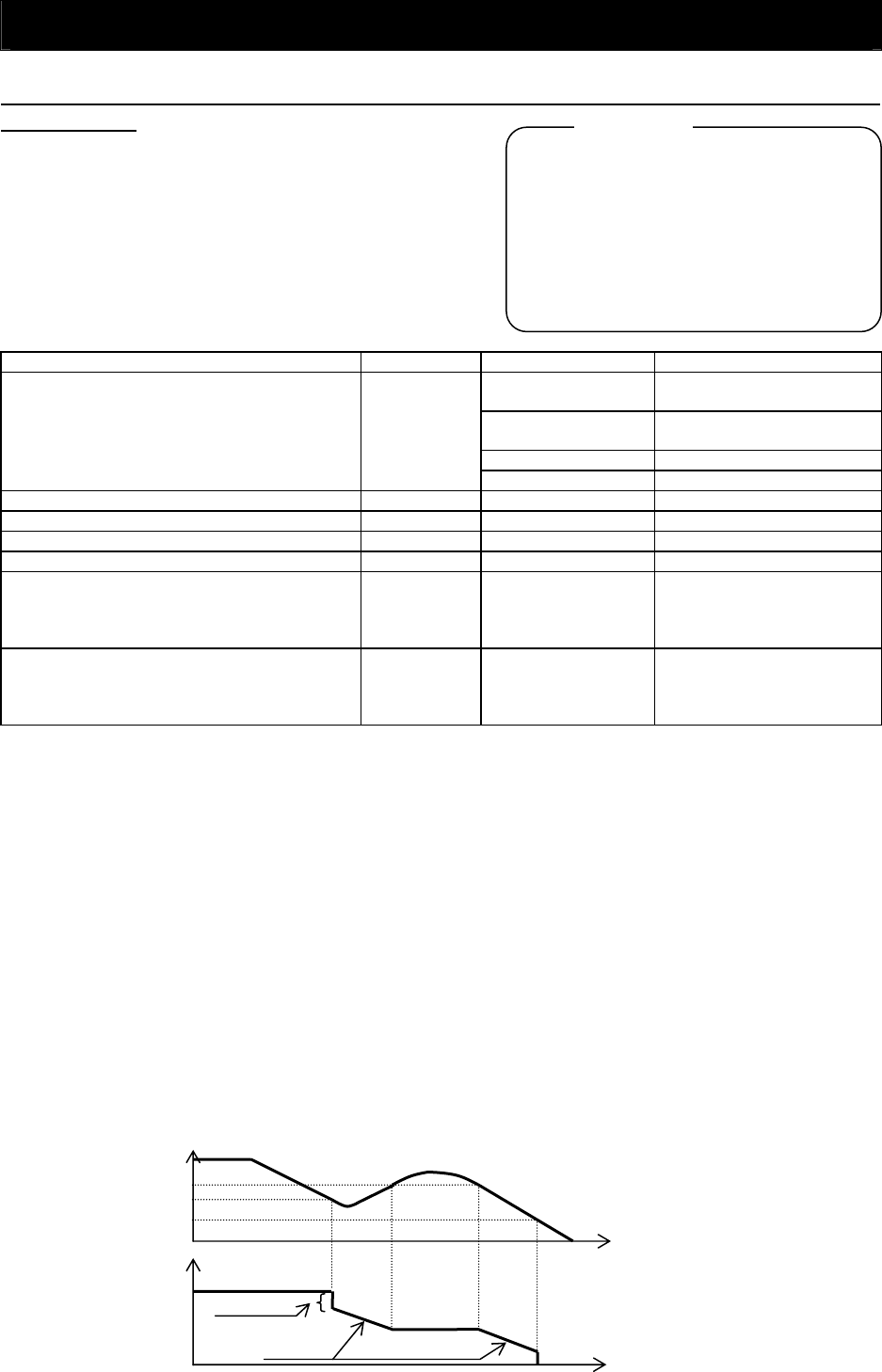
<1> nonstop deceleration at instantaneous power failure (b050=01)
b050: Controller deceleration and stop on power loss
b051: DC bus voltage trigger level during power loss
b052: Over-voltage threshold during power loss
b053: Deceleration time setting during power loss
b054: Initial output frequency decrease during power
loss Integral time setting for nonstop operation at
momentary power failure
b055: Proportional gain setting for nonstop operation
at momentary power failure
b056: Integral time setting for nonstop operation at
momentary power failure
- The nonstop deceleration at instantaneous power failure is the function making the inverter decelerate
and stop the motor while maintaining the voltage below the overvoltage level (over-voltage threshold
during power loss [b052]) when an instantaneous power failure occurs during the inverter operation.
- To use this function, remove the J51 connector cables from terminals R0 and T0, connect the main circuit
terminals P and R0 to each other, and connect the main circuit terminals N and T0 to each other. Use
0.75 mm2 or heavier wires for the connections.
- If an instantaneous power failure has occurred while the inverter is operating the motor and the output
voltage falls to the DC bus voltage trigger level during power loss (b051) or less, the inverter reduces the
output frequency by the initial output frequency decrease during power loss (b054) once, and then
decelerates the motor for the deceleration time setting during power loss (b053).
- If the voltage increases to an overvoltage level (exceeding the over-voltage threshold during power loss
[b052]) because of regeneration, the inverter enters the LAD stop state until the voltage falls below the
overvoltage level.
Note1:If the over-voltage threshold during power loss (b052) is less than the DC bus voltage trigger level
during power loss (b051), the over-voltage threshold during power loss will be increased to the DC
bus voltage trigger level during power loss when the stop level is applied. (However, the stored
setting will not be changed.)
Note2:This nonstop deceleration function cannot be canceled until the nonstop deceleration operation is
completed. To restart the inverter operation after power recovery, wait until the inverter stops, enter
a stop command, and then enter an operation command.
Note3:Setting higher initial out put frequency decrease during powerloss
(b054) results in over current trip due to sudden deceleration.
Setting lower b054, orlonger deceleration time
during powerloss (b053) results in
undervoltage trip due to less
regeneration power.
Related code
b052
b051
b053
b054
VPN(V)
V
oltage across main circuit
terminals P and N
Undervoltage level
Output frequency
(Hz)
Time
(
sec
)
Time (sec)


















