Chapter 4 Explanation of Functions
4 - 84
- If momentary power failure occurs or the main circuit DC voltage drops during inverter operation, the
inverter decelerates the motor while maintaining the main circuit DC voltage at the level specified as the
target nonstop operation voltage at momentary power failure (0V-LAD stop level) (b052).
<2> DC voltage constant control during nonstop operation at momentary power failure (b050 = 02: no
restoration, b050 = 03: restoration to be done)
- This function starts operating when all the following conditions are met:
-- "02" or "03" has been specified for b050.
-- The inverter is running. (This function does not operate if the inverter has been tripped, is in
undervoltage status or stopped.)
-- The control power fails momentarily or the main circuit DC voltage drops to the DC bus voltage
trigger level during power loss (b051) or less.
- This function operates when the conditions above are met even if the J51 connector cables have been
disconnected from terminals R0 and T0, and cables are connected from main circuit terminal P to
terminal R0, and from main circuit terminal N to terminal T0.
- If momentary power failure only lasts a short time, the inverter can continue operation without stopping its
output. Conversely, if momentary power failure causes undervoltage, the inverter stops its output
immediately and ends the operation of this function. When power is subsequently restored, the inverter
operates according to the selection of restart mode (b001).
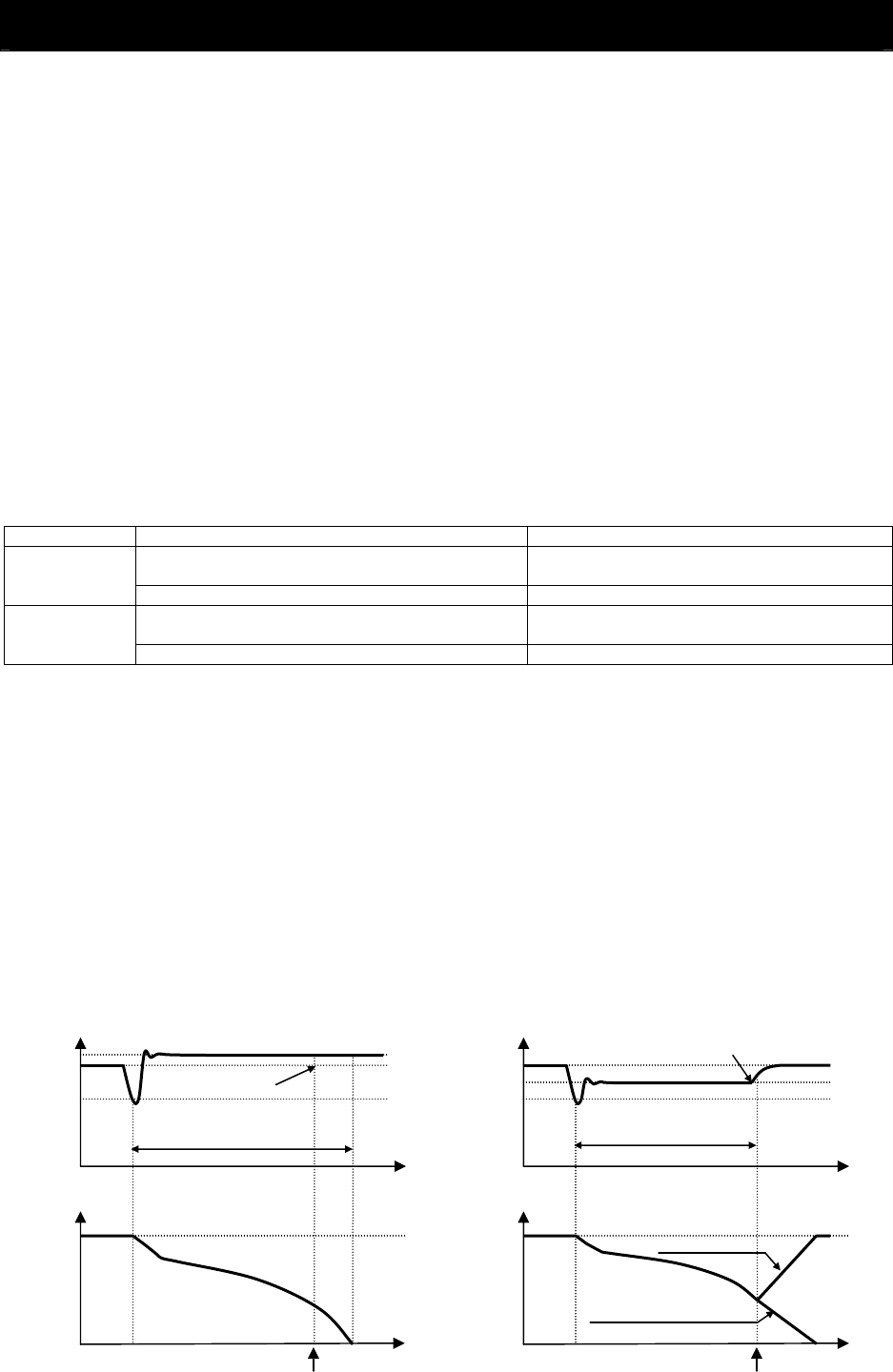
- When "03" is specified for b050, the inverter can be restored to normal operation if the input power is
recovered from momentary power failure before the inverter stops its output. The inverter, however, may
decelerate and stop the motor if a specific setting has been made for b051. The table below lists the
differences in operation according to the setting of b051.
b050 b051 Operation
b052 > Main circuit DC voltage at input power recovery
Decelerating and stopping the motor (DC voltage
constant control) (Example 1)
02 (No
restoration)
b052 < Main circuit DC voltage at input power recovery Decelerating and stopping the motor (Example 2)
b052 > Main circuit DC voltage at input power recovery
Decelerating and stopping the motor (DC voltage
constant control) (Example 1)
03 (Restoration
to be done)
b052 < Main circuit DC voltage at input power recovery Decelerating and stopping the motor (Example 2)
- When this function operates and the inverter decelerates and stops the motor, the motor is forcibly
stopped even if the FW signal is on. To restart the motor, turn on the FW signal again after confirming the
recovery of inverter input power.
Note 4: Each of the values of b051 and b052 must be the undervoltage 210V(200V class),410V(400V
class)level or more. This function does not operate when undervoltage occurs. The value of b051 must
be less than that of b052. When b051 is much higher proportional gain (b055) results in overcurrent by
rapid acceleration after this function operates.
Note 5: When "02" or "03" is specified for b050, PI control is performed so that the internal DC voltage is
maintained at a constant level.
- Setting a higher proportional gain (b055) results in a faster response. However, an excessively high
proportional gain causes the control to diverge and results in the inverter easily tripping.
- Setting a shorter integral time (b056) results in a faster response. However, an excessively short integral
time results in the inverter easily tripping.
- Setting a lower proportional gain (b055) results in undervoltage trip due to a voltage drop immediately
after starting this function.
b050=02
(decelerate to stop)
Period of DC voltage
constant control
Voltage across main circuit terminals P and N
Vpn(V)
Time
Time
Output frequency
(Hz)
b050=03(running)
b052
b051
Voltage across main circuit terminals P and N
Vpn(V)
Time
Time
Output frequency
(Hz)
Period of DC voltage
constant control
b050=02,03
(decelerate to stop)
DC voltage across main circuit
Recovery of input power
b052
b051
(Example 1)
(Example 2)
DC voltage across main circuit
Recovery of input power
Recovery of input power Recovery of input power


















