Chapter 6 Maintenance and Inspection
6.8 Methods of Measuring the Input/Output Voltages, Current, and Power
This section describes the measuring instruments generally used to measure the input and output voltages,
output current, and output power of the inverter.
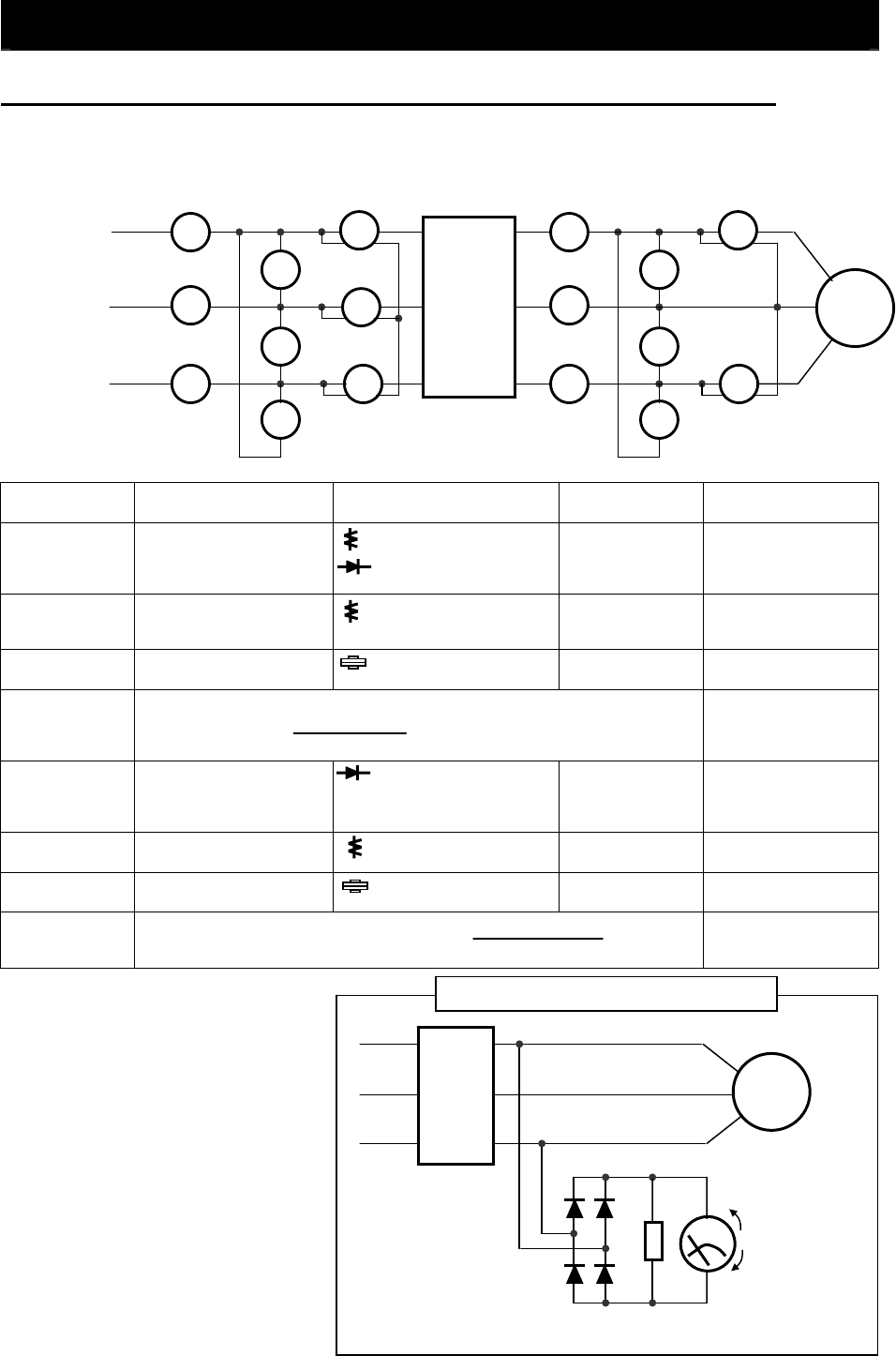
I
R
I
S
I
T
E
R
E
T
E
S
W
I2
W
I3
W
I1
R
T
S
U
V
W
I
U
I
V
I
W
E
U
E
W
E
V
W
O2
W
O1
W
V
U R
S
T
Power supply
Inverter
Motor
Measurement
item
Measuring point Measuring instrument Remarks Reference values
Input voltage (E
IN
) Across R-S, S-T, and T-R
(E
R
), (E
S
), and (E
T
)
Moving-iron voltmeter
or
rectifier-type voltmeter
Effective value of
full waves
200 V class models:
200 to 240 V, 50/60 Hz
400 V class
380 to 480 V, 50/60 Hz
Input current (I
IN
) Current at R, S, and T
(I
R
), (I
S
), and (I
T
)
Moving-iron ammeter Effective value of
full waves
When input currents are
unbalanced
I
IN
= (I
R
+ I
S
+ I
T
)/3
Input power (W
IN
) Across R-S, S-T, and T-R
(W
11
) + (W
12
) + (W
13
)
Electrodynamometer-type
wattmeter
Effective value of
full waves
3-wattmeter method
input power factor
(Pf
IN
)
Calculated from the measured input voltage (E
IN
), input current (I
IN
), and input power
(W
IN
)
Output voltage
(E
OUT
)
Across U-V, V-W, and W-U
(E
U
), (E
V
), and (EW)
Method shown in the figure
below
or
rectifier-type voltmeter
Effective value of
fundamental wave
Output current
(I
OUT
)
Current at U, V, and W
(I
U
), (IV), and (IW)
Moving-iron ammeter Effective value of
full waves
Output power
(W
OUT
)
Across U-V and V-W
(W
01
) + (W
02
)
Electrodynamometer-type
wattmeter
Effective value of
full waves
2-wattmeter method
(or 3-wattmeter method)
6 - 6
W
IN
×100(%)
√3・EIN・IIN
Pf
IN
=
Output power
factor (Pf
OUT
)
Calculated from the measured input
voltage (E
OUT
), input current (I
OUT
),
and input power (W
OUT
)
PfOUT=
W
OUT
√3・EOUT・IOUT
×100(%)
Notes:
1. To measure the output voltage, use
an instrument that reads the
effective value of the fundamental
wave. To measure the current or
power, use an instrument that reads
the effective value of full waves.
2. Since the inverter output waveform
is controlled by PWM, it has a large
margin of error, especially at low
frequencies. In many cases, general
testers may be inapplicable for the
measurement because of the
adverse effect of noise.
Diode
600 V, 0.1 A or more
(200 V class model)
1,000 V, 0.1 A or more
(400 V class model)
Effective value of
fundamental wave (V
AC
)
V
AC
= 1.1 x V
DC
R
T
S
Inverter
U
V
W
Motor
2W 220kΩ
Moving-coil voltmeter
300 V (200 V class
model)
600 V (400 V class
model
)
VDC
-
+
Method to measure the output voltage