Chapter 4 Explanation of Functions
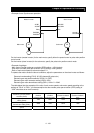
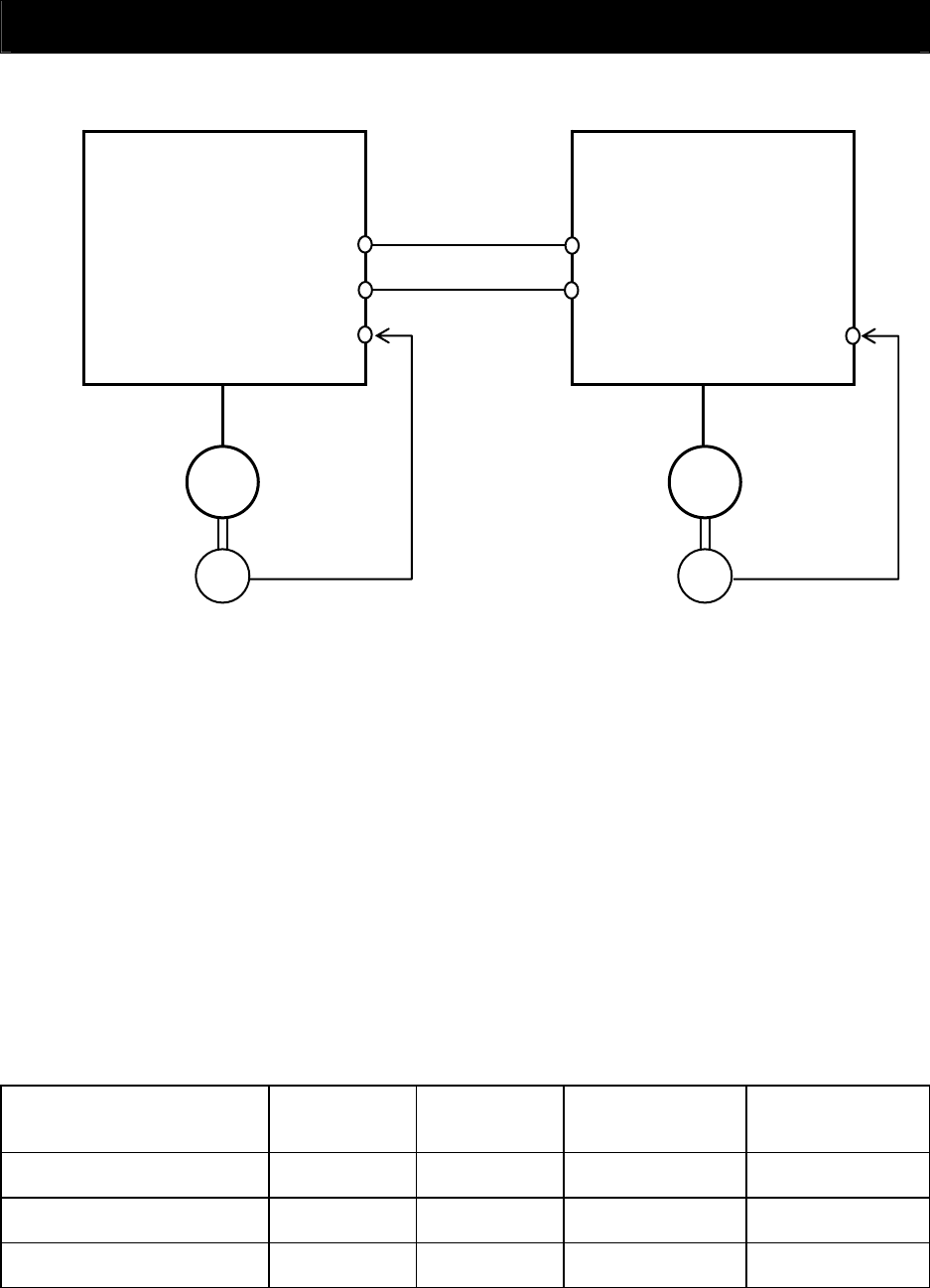
<Example of use: Synchronous operation>
Master inverter Slave inverter
EAP,EBP
EAN,EBN
SAP,SBP
SAN,SBN
EG5
EAP,EBP
EAN,EBN
EC
M
EC
M
AP,BP
AN,BN
EG5
Sub-motor
Main motor
On the inverter (master inverter) for the main motor, specify either the speed control or pulse train position
control mode.
On the inverter (slave inverter) for the sub-motor, specify the pulse train position control mode.
<Example of settings>
- Main motor: Encoder pulse-per-revolution (PPR) setting = 1024 (pulses)
- Sub-motor: Encoder pulse-per-revolution (PPR) setting = 3000 (pulses)
- Ratio of main motor speed to sub-motor speed: 2:1
To operate the motors under the above conditions, adjust the parameters on the slave inverter as follows:
Pulse train mode setting (P013): 00 (90º-phase-shift pulse train)
Electronic gear set position selection (P019): 01 (REF)
Electronic gear ratio numerator setting (P020): 3000
Electronic gear ratio denominator setting (P021): 1024 x 2 = 2048
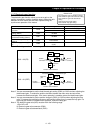
The table below lists the examples of the ratio of main motor speed to sub-motor speed according to the
settings of "P019" to "P021" (on the assumption that the encoder pulse-per-revolution (PPR) setting of
"1024" should be set on both inverters).
Electronic gear set position
selection (P019)
REF
(Position
command side)
REF
(Position
command side)
FB
(Position feedback
side)
FB
(Position feedback
side)
Electronic gear ratio numerator
setting (P020)
1024 2048 1024 2048
Electronic gear ratio
denominator setting (P021)
2048 1024 2048 1024
Sub-motor speed/main motor
speed
1/2 2 2 1/2
4 - 104