Chapter 4 Explanation of Functions
4.2.17 V/F characteristic curve selection
The V/F characteristic curve selection function allows you to set
the output voltage/output frequency (V/f) characteristic.
A044/A244/A344: V/F characteristic curve
selection, 1st/2nd/3rd motors
b100/b102/b104/b106/b108/b110/b112:
Free-setting V/f frequency (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7)
b101/b103/b105/b107/b109/b111/b113:
Free-setting V/f voltage (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7)
Related code
To switch the V/F characteristic curve selection among the 1st,
2nd, and 3rd settings, assign function "08" (SET) and "17"
(SET3) to intelligent input terminals. Use the SET and SET3
signals for switching.
Function code Data V/f characteristic Remarks
00 Constant torque characteristic (VC)
01
Reduced-torque characteristic
(1.7th power of VP)
02 Free V/f characteristic Available only for A044 and A244
03
Sensorless vector control (SLV) Available only for A044 and A244 (See Section
4.2.96.)
04
0 Hz-range sensorless vector
control
Available only for A044 and A244 (See Section
4.2.97.)
A044/A244/
A344
05 Vector control with sensor (V2) Available only for A044
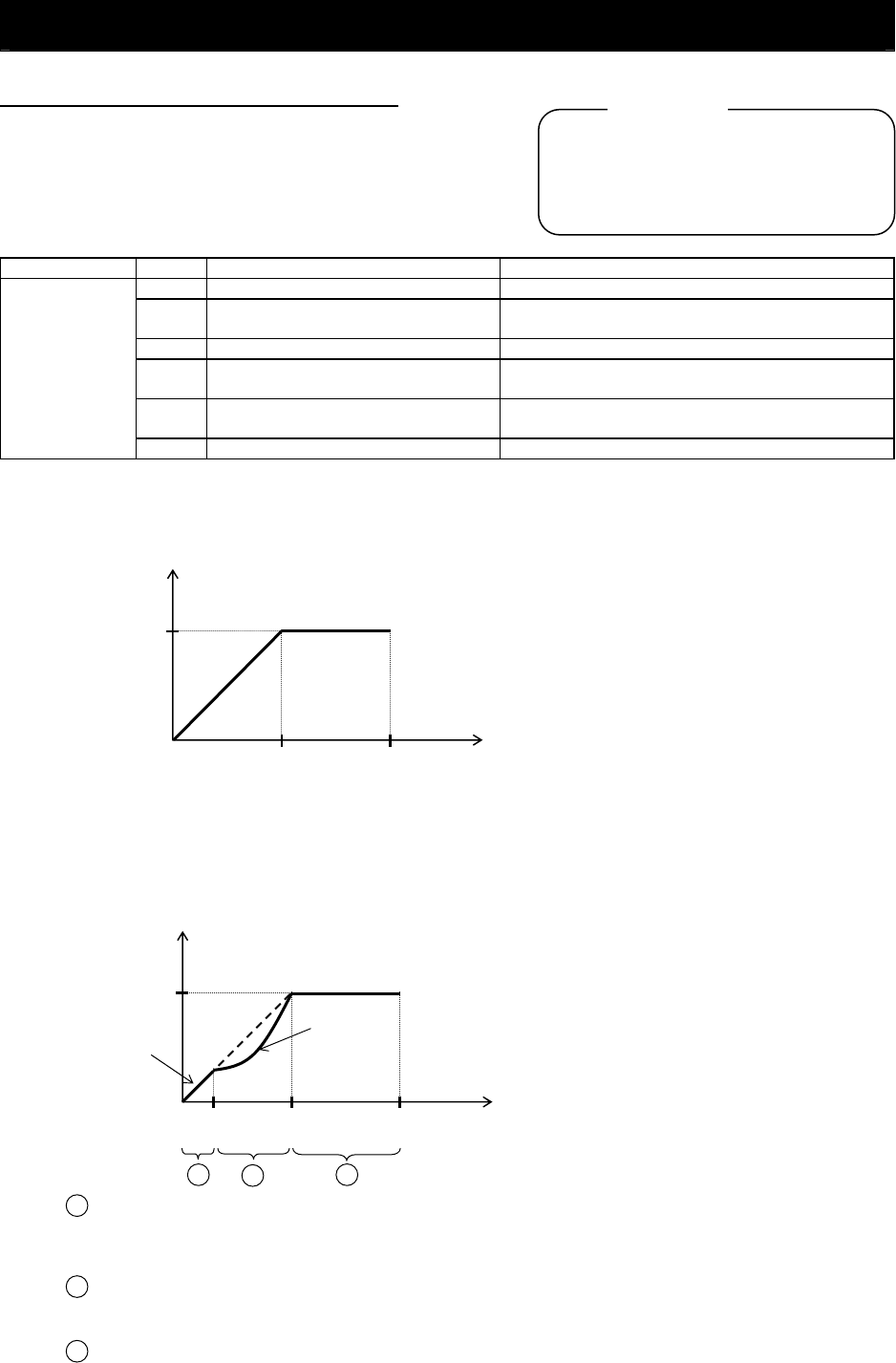
(1) Constant torque characteristic (VC)
With this control system set, the output voltage is in proportion to the output frequency within the range
from 0 Hz to the base frequency. Within the output frequency range over the base frequency up to the
maximum frequency, the output voltage is constant, regardless of the change in the output frequency.
0
Output voltage
(100%)
Base
frequency
Maximum
frequency
Output frequency (Hz)
(2) Reduced-torque characteristic (1.7th power of VP)
This control system is suited when the inverter is used with equipment (e.g., fan or pump) that does not
require a large torque at a low speed.
Since this control system reduces the output voltage at low frequencies, you can use it to increase the
efficiency of equipment operation and reduce the noise and vibrations generated from the equipment.
The V/f characteristic curve for this control system is shown below.
0
VP
(f
1.7
)
VC
a
b
c
Output voltage
(100%)
Base
frequency
Maximum
frequency
Output frequency (Hz)
10% of base
frequency
Period : While the output frequency increases from 0 Hz to the 10% of the base frequency, the
output voltage follows the constant torque characteristic.
a
(Example) If the base frequency is 60 Hz, the constant torque characteristic is maintained
within the output frequency range of 0 to 60 Hz.
Period : While the output frequency increases from the 10% of base frequency to the base
frequency, the output voltage follows the reduced-torque characteristic. In other words, the
output voltage increases according to the 1.7th power of the output frequency.
b
Period : While the output frequency increases from the base frequency to the maximum frequency,
the output voltage is constant.
c
4 - 16