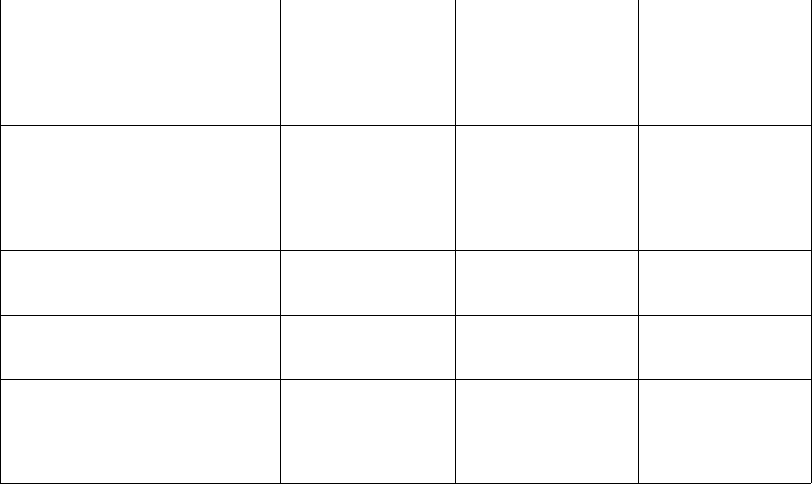
An ANSI (non-UniTree) or
HPSS label with a correct
Volume ID (the Volume ID on
the label is as expected by
HPSS)
Tape Imported Label Written,
Tape Imported
Tape Imported
An ANSI or HPSS label with
an incorrect Volume ID (the
Volume ID on the label is
different from the Volume ID
expected by HPSS)
Tape Not Imported Tape Not Imported Tape Not Imported
Random data (e.g., a tar file) Tape Not Imported Label Written,
Tape Imported
Label Written,
Tape Imported
No data (two tapemarks at the
start of tape)
Label Written,
Tape Imported
Label Written,
Tape Imported
Label Written,
Tape Imported
Unreadable (e.g., some brand
new tapes or a degaussed tape;
also possibly a tape written at a
different density)
Tape Not Imported Label Written,
Tape Imported
Label Written,
Tape Imported
HPSS always attempts to read a label at the beginning of a tape when performing an import. Some tape
drives and device drivers will report errors when asked to read unreadable tapes (as described above). If
this happens, manually write two tape marks at the start of the tape and retry the import. Most UNIX
systems provide the mt command, which can be used to write tape marks.
An HPSS label is basically just an ANSI label. A few characters are changed to identify the tape as
having been labeled by HPSS. Both label types are supported by HPSS; tapes already beginning with an
ANSI label are not relabeled unless the overwrite import option is selected and volume labels match.
8.1.1.3. Import Disk Volumes Window
HPSS Management Guide November 2009
Release 7.3 (Revision 1.0) 230


















