WR3000 4-Port Wireless DSL/Cable Router
®
41
6.2 Wireless LAN Basics
6.2.1 RTS/CTS
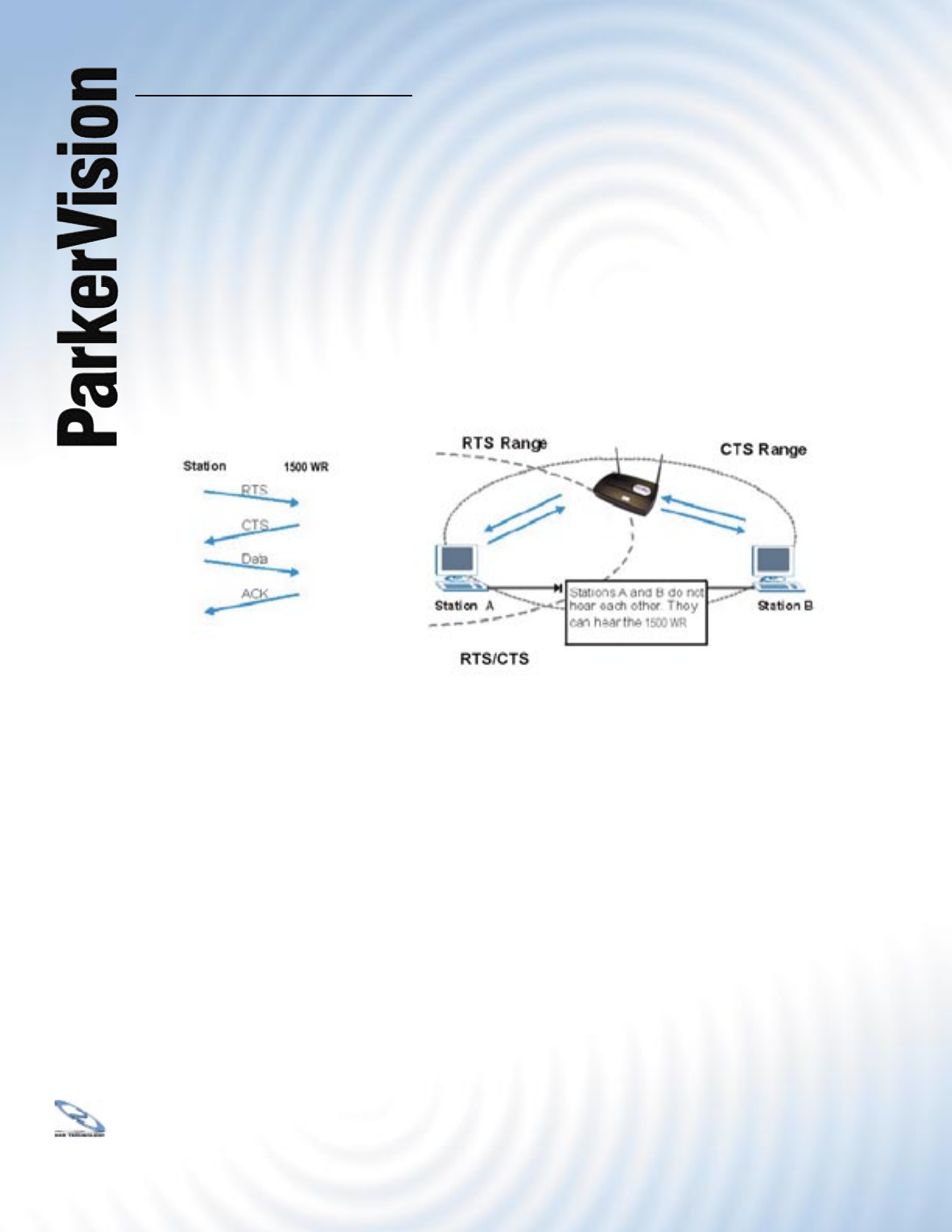
A hidden node occurs when two stations are within range of the same Wireless Router, but
are not within range of each other. The following fi gure illustrates a hidden node. Both stations
(STA) are within range of the Wireless Router (AP) or wireless gateway, but out-of-range of
each other, so they cannot “hear” each other, that is they do not know if the channel is currently
being used. Therefore, they are considered hidden from each other.
When station A sends data to the WR3000 Wireless Router, it might not know that station B
is already using the channel. If these two stations send data at the same time, collisions may
occur when both sets of data arrive at the AP at the same time, resulting in a loss of messages
for both stations.
RTS/CTS is designed to prevent collisions due to hidden nodes. An RTS/CTS defi nes the
biggest size data frame you can send before an RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send)
handshake is invoked.
When a data frame exceeds the RTS/CTS value you set (between 0 to 2432 bytes), the station
that wants to transmit this frame must fi rst send an RTS (Request To Send) message to the
AP for permission to send it. The AP then responds with a CTS (Clear to Send) message to
all other stations within its range to notify them to defer their transmission. It also reserves and
confi rms with the requesting station the time frame for the requested transmission.
Stations can send frames smaller than the specifi ed RTS/CTS directly to the AP without the
RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake.
You should only confi gure RTS/CTS if the possibility of hidden nodes exists on your network
and the “cost” of resending large frames is more than the extra network overhead involved in
the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake.
If the RTS/CTS value is greater than the Fragmentation Threshold value (see next), then the
RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake will never occur as data frames will
be fragmented before they reach RTS/CTS size.
Enabling the RTS Threshold causes redundant network overhead that could
negatively affect the throughput performance instead of providing a remedy.


















