WR3000 4-Port Wireless DSL/Cable Router
®
44
6.4 Confi guring Roaming
A wireless station is a device with an IEEE 802.1 lb compliant wireless adapter. An access point
(AP) acts as a bridge between the wireless and wired networks. An AP creates its own wireless
coverage area. A wireless station can associate with a particular access point only if it is within
the access point’s coverage area.
In a network environment with multiple access points, wireless stations are able to switch from
one access point to another as they move between the coverage areas. This is roaming. As the
wireless station moves from place to place, it is responsible for choosing the most appropriate
access point depending on the signal strength, network utilization or other factors.
The roaming feature on the access points allows the access points to relay information about
the wireless stations to each other. When a wireless station moves from a coverage area to
another, it scans and uses the channel of a new access point, which then informs the access
points on the LAN about the change. The new information is then propagated to the other
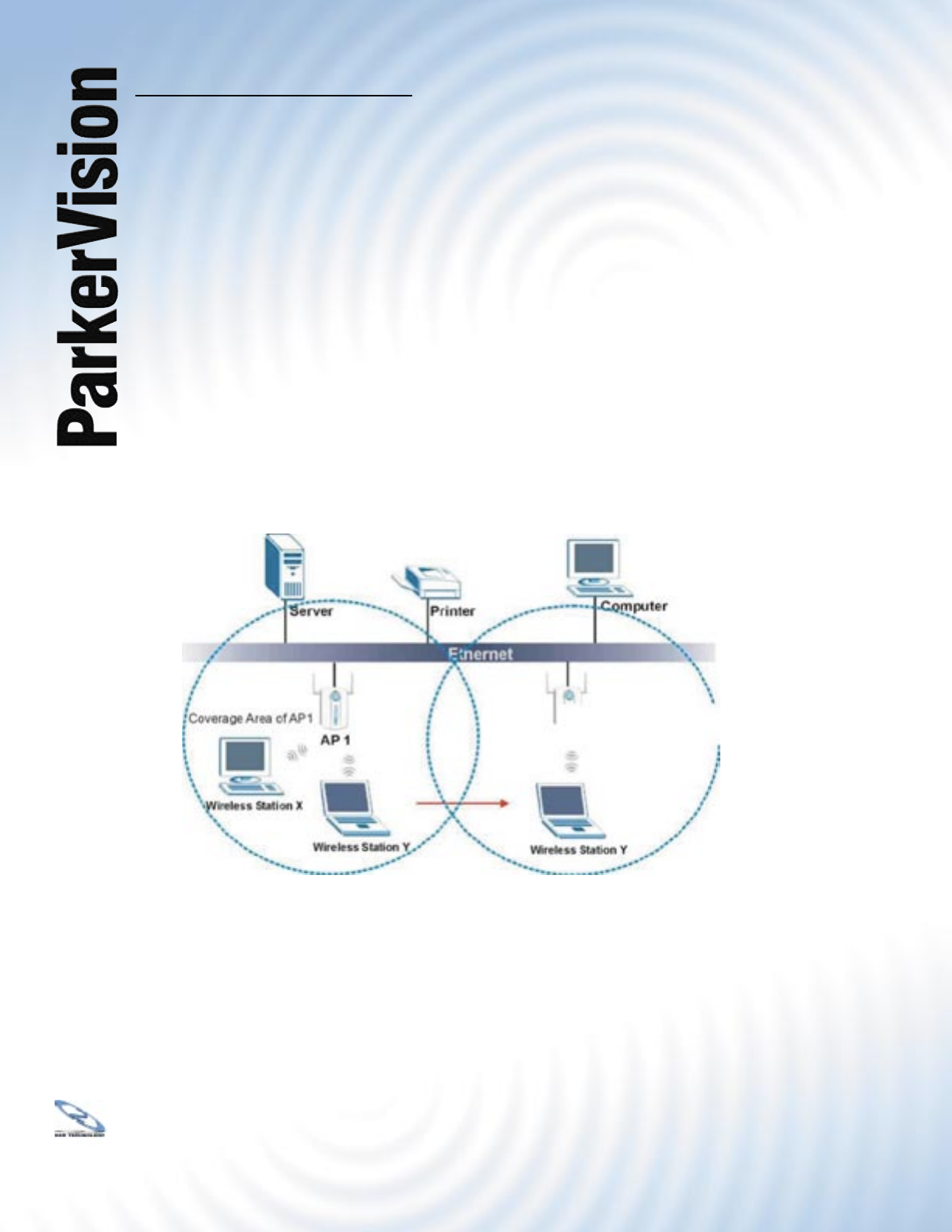
access points on the LAN. An example is shown in Figure 6.4.1. If the roaming feature is not
enabled on the access points, information is not communicated between the access points
when a wireless station moves between coverage areas. The wireless station may not be able
to communicate with other wireless stations on the network and vice versa.
6.4.1 Roaming Example
The steps below describe the roaming process.
Step 1. As wireless station Y moves from the coverage area of access point AP 1 to that
of access point AP 2, it scans and uses the signal of access point AP 2.
Step 2. Access point AP 2 acknowledges the presence of wireless station Y and relays
this information to access point AP 1 through the wired LAN.
Step 3. Access point AP 1 updates the new position of wireless station.
Step 4. Wireless station Y sends a request to access point AP 2 for re-authentication.


















