EW_INTCTL[1]
EW_INTCTL[2]
EW_INTCTL[3]
EW_INTCTL[4]
EW_INTCTL[4:1]
MACINT
Commoninterruptcombinerblock
HOST
STAT
MDIO_LINT
MDIO_USER
www.ti.com
EMAC Functional Architecture
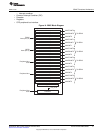
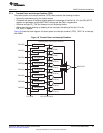
2.7.6 Common Interrupt Combiner (CIC)
The common interrupt combiner (CIC) block performs following functions:
• Combines the two common interrupts from EMAC (HOST and STAT) with the two MDIO interrupts
(MDIO_LINT and MDIO_USER) and generates a single MACINT interrupt per theC64x+ megamodule.
• Performs a level-to-pulse conversion of the interrupts because the interrupts from EMAC and MDIO
are level sensitive and the C64x+ megamodule expects a pulse interrupt.
• Allows, per interrupt enabling or disabling of the interrupts, the setting of bits 1 to 4 in the EW_INTCTL
register.
Figure 20 is the block diagram representing common interrupt combiner.
Figure 20. Common Interrupt Combiner
2.8 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) Module
The Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) module manages up to 32 physical layer (PHY) devices
connected to the Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC). The MDIO module allows almost transparent
operation of the MDIO interface with little maintenance from the CPU.
The MDIO module enumerates all PHY devices in the system by continuously polling 32 MDIO addresses.
Once it detects a PHY device, the MDIO module reads the PHY status register to monitor the PHY link
state. The MDIO module stores link change events that can interrupt the CPU. The event storage allows
the CPU to poll the link status of the PHY device without continuously performing MDIO module accesses.
However, when the system must access the MDIO module for configuration and negotiation, the MDIO
module performs the MDIO read or write operation independent of the CPU. This independent operation
allows the DSP to poll for completion or interrupt the CPU once the operation has completed.
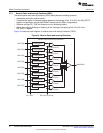
2.8.1 MDIO Module Components
The MDIO module (shown in Figure 21) interfaces to PHY components through two MDIO pins (MDCLK
and MDIO), and to the DSP core through the EMIC module and the configuration bus. The MDIO module
consists of the following logical components:
• MDIO clock generator
• Global PHY detection and link state monitoring
• Active PHY monitoring
• PHY register user access
47
SPRUEF8F–March 2006–Revised November 2010 C6472/TCI6486 EMAC/MDIO
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2006–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated