3 – Planning
Device Access
3-2 59043-06 A
0
3.2
Device Access
Consider device access needs within the fabric. Access is controlled by the use of
zones and zone sets. Some zoning strategies include the following:
Group devices by operating system.
Separate devices that have no need to communicate with other devices in
the fabric or have classified data.
Separate devices into department, administrative, or other functional group.
Reserve a path and its bandwidth from one port to another.
A zone is a named group of devices that can communicate with each other.
Membership in a zone can be defined by switch domain ID and port number, port
Fibre Channel address, or by device worldwide name (WWN). Devices can
communicate only with devices within the same zone. The SANbox2-64 switch
supports both hard and soft zones. A zone can be a member of more than one
zone set. Several zone sets can be defined for a fabric, but only one zone set can
be active at one time. The active zone set determines the current fabric zoning.
A zoning database is maintained on each switch consisting of all inactive zone
sets, the active zone set, all zones, aliases, and their membership. Table 3-1
describes the zoning database limits, excluding the active zone set. Refer to the
SANbox2-64 Switch Management User’s Guide for more information about
zoning.
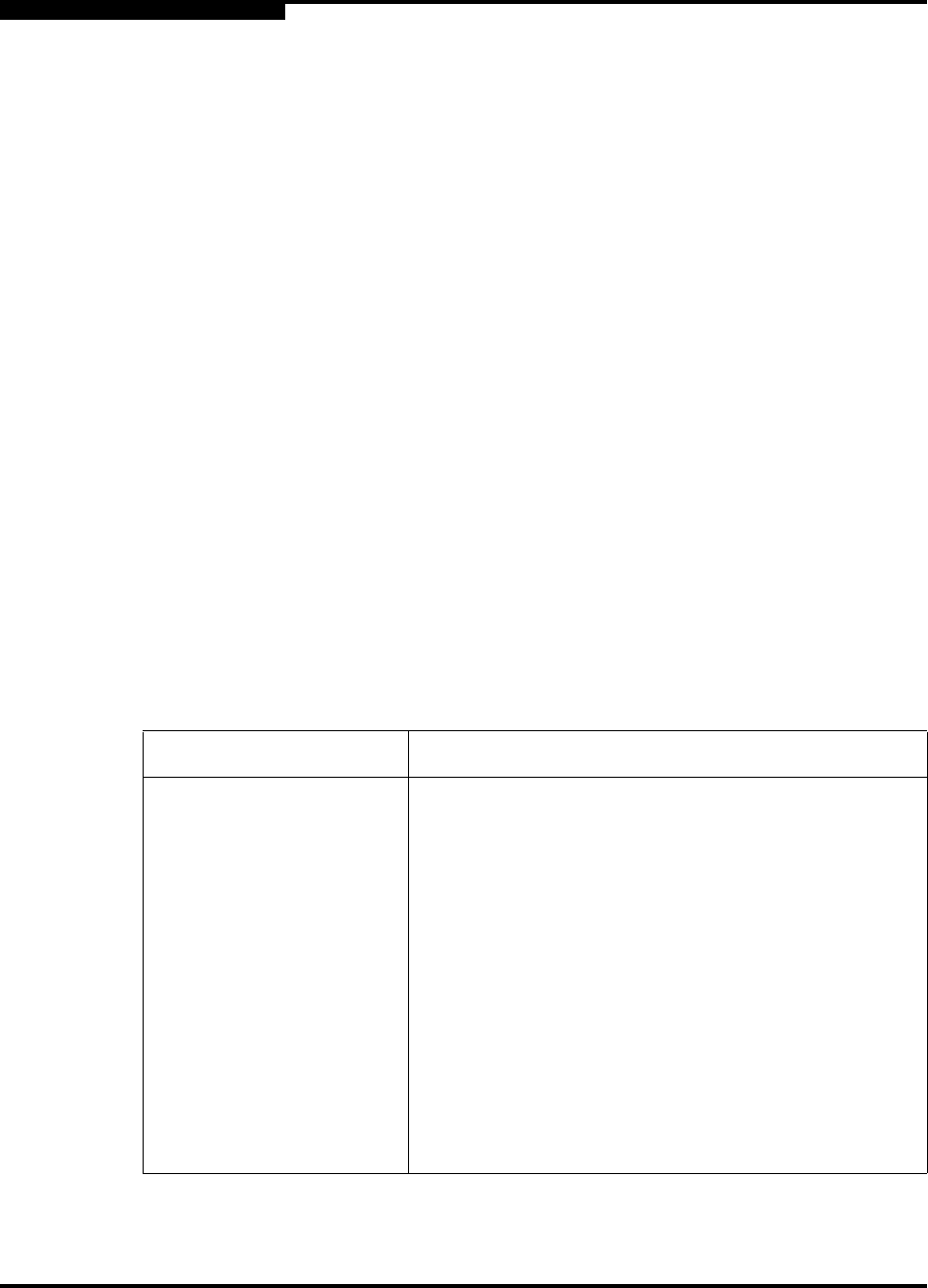
Table 3-1. Zoning Database Limits
Limit Description
MaxZoneSets Maximum number of zone sets (256).
MaxZones Maximum number of zones (1000).
MaxAliases Maximum number of aliases (2500).
MaxTotalMembers Maximum number of zone and alias members (10000)
that can be stored in the switch’s zoning database.
MaxZonesInZoneSets Maximum number of zones that are components of
zone sets (1000), excluding the orphan zone set, that
can be stored in the switch’s zoning database. Each
instance of a zone in a zone set counts toward this
maximum.
MaxMembersPerZone Maximum number of members in a zone (2000)
MaxMembersPerAlias Maximum number of members in an alias (2000)


















