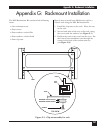
Multiserver 5000
252
ABR, autobaud rate detection — A process by which
a receiving device determines the data rate,
code level, and stop bits of incoming data by
examining the first character received (usually a
preselected sign-on character). ABR allows a
receiving device to accept data from a variety of
transmitting devices operating at different data
rates, which means that the receiver does not
need to be configured for each specific data
rate in advance.
ACK, acknowledgment — A control character used
as a reply in communications protocols. For
example, in the Hewlett-Packard ENQ/ACK
protocol, ACK is sent by the receiving device as a
reply to ENQ sent by the transmitting device.
ADB, automatic dial backup — A modem feature
that enables it to automatically switch data
transmission from the leased lines to dial lines
when line impairments on the leased lines reach
an unacceptable level. The modem also returns
to leased-line operation when the conditions of
those lines improve.
aggregate input rate — The sum of all data rates of
terminals and computer ports connected to a
multiplexer. “Burst aggregate input rate” is the
instantaneous maximum data input rate
accepted by the multiplexer.
analog — Continuously variable as opposed to
discretely variable. Physical quantities, such as
temperatures, are continuously variable and are
described as analog; analog signals vary in
accordance with the physical quantities they
represent. The public telephone network was
designed to transmit voice in analog form.
analog loopback — A diagnostic test that forms the
loop at the modem’s telephone line interface.
answer tone — A signal sent by the called modem
(the answer modem) to the calling modem (the
originate modem) on public telephone
networks that indicates the called modem’s
readiness to accept data.
answer tone frequency — The frequency (cycles per
second) of the answer tone.
APV, Advanced Packetized Voice — Low Bit Rate
Voice (LBRV) digitizing technique that
produces acceptable-quality voice signals and
requires a bandwidth of only 9.6 Kbps.
ARQ, automatic request for retransmission — An
error-control method in which the receiving
device informs the transmitting device which
transmission blocks were received successfully.
The transmitting device retransmits any blocks
not successfully received.
ASCII, American Standard Code for Information
Interchange — A 7-bit-plus-parity character set
or code established by the American National
Standards Institute (ANSI) to achieve
compatibility between data services.
async — Short for asynchronous. See asynchronous
transmission.
asynchronous transmission — A method of sending
data in which the interval between characters
may be of unequal length. The characters
transmitted include a start bit and one or more
stop bits, which define the beginning and
ending of the character. No synchronizing or
timing signals need to be sent.
attenuation — Deterioration of signal strength as it
passes through a transmission medium;
generally attenuation increases with both
frequency and cable length. Attenuation is
measured in terms of decibels.
bar graph — A visual indication of the input signal
level strength in dB, as displayed on the
command port or by the four red indicators on
the voice/fax channel.
baud — A unit of signalling speed. The speed in
baud is the number of discrete conditions or
signal events per second. If each signal event
represents one bit, the baud rate is the same as
bps. If each signal event represents more than
Glossary