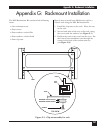
Multiserver 5000
254
channel — A path for electrical transmission
between two or more points without common
carrier-provided terminal equipment such as a
local connection to DTE. Also called circuit,
line, data link, or path. It may be asynchronous,
synchronous, or voice.
channel number — The channel number describes
a specific module location and connector and is
used in the configuration process. For example,
the CCM has six channel numbers: A1 through
A6.
channel loopback — A diagnostic test that forms the
loop at the multiplexor’s channel interface.
character — A letter, number, punctuation, or other
symbol contained in a message. See also control
character.
circuit — In data communications, a means of two-
way communication between two points,
consisting of transmit and receive channels. In
electronic design, one or more components that
act together to perform one or more functions.
class — A name given to a group of one or more
async channels. The maximum number of
classes available on the Multiserver unit is 64.
Classes are used to group similar channels for
network users and may be viewed as a hunt
group where an async user can connect to any
available ports/channels in the group.
clock — The timing signal used in synchronous
transmission. Also, the source of such timing
signals.
code — A set of rules that specifies the way data is
represented, such as ASCII or EBCDIC.
code level — The number of bits used to represent
characters.
cold start — Performed in either the Command
Facility or at the LCD/Keypad, a cold start (or
cold reset) is a system reset which returns the
unit to the factory defaults.
Command Facility — a menu-driven structure
containing all the configuration options.
Command Mode — a menu-driven structure that
supports all the configuration, diagnostics, and
system administrative functions.
command port — A dedicated terminal used to
control and monitor a multiplexer system. Also,
the interface to which this terminal is
connected.
CommPak cartridge — A cartridge that contains the
operating software for a Multiserver or a
compatible multiplexor.
communications protocol — The means used to
control the orderly exchange of information
between stations on a data link or on a data
communications network or system. Also called
line discipline or protocol.
composite — The line-side signal of a multiplexer
that includes all the multiplexed data, including
asynchronous and synchronous data as well as
digitized voice. Also known as a link.
composite loopback — A diagnostic test that forms
the loop at the line side (output) of a
multiplexer.
compression — A method for reducing the number
of data and voice bits across a link, thus
reducing bandwidth requirements.
conditioning — The tuning or addition of
equipment to improve the transmission
characteristics or quality of a leased voice-grade
line so that it meets specifications for data
transmission. The customer pays a monthly
charge for conditioning.
configuration switch group — See switch group.
connection — An established data-communications
path, the process of establishing that path, or a
point of attachment for that path.
connector — An electrical device for making one or
more connections.
control character — A non-printing character used
to start, stop, or modify a function.
control signal — An interface signal used to
indicate, start, stop, or modify a function.