Multiserver 5000
70
8.1 Types of Links
There are three types of links in the Multiserver
system:
An Interconnect Link connects two Multiservers
(usually over an analog or digital circuit
provided by the telephone company).
A Mux Link connects a Multiserver to a
compatible multiplexer. The Feeder Mux can be
connected directly to the Multiserver or
remotely using a line driver, modem, or ISU.
An X.21 Link connects a Multiserver to a
compatible multiplexer via an X.21 bis network.
8.2 Avoid Node Duplication
Your local node should already be named (see
Section 6.6, Name the Local Node). To avoid
duplication of a node number or ID in a string, V,
or star network, connect one link at a time. After
each link is connected, access the remote node to
configure its node number and ID. Then connect
the next link.
NOTE: Depending on how your network will be
configured, it may not be possible to do all
network configurations from one node. You
might have to name and configure each node
independently before installing the links.
If a link is established between two Multiservers that
have the same node number or ID, a DUPLICATE
NODE-ID error message will be displayed.
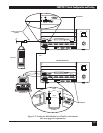
8.3 Assign a Port for Each Link
Each link must be attached to a port on the CCM.
Interconnect links should be configured on the
lower-most channels (i.e., A1, then A2), followed by
mux and X.21 links, then sync channels, and finally
async channels. Configuring the node in this
manner will yield optimum performance. See the
example in Figure 8-1.
NOTE: When the CSU/DSU module is installed and
operational, it is considered attached to port
A1. All configurations for port A1 directly
affect the CSU/DSU module. The A1 LED
indicator will go off when the interconnect
link attached to the CSU/DSU module is
functioning properly.
8. Link Configuration
MULTISERVER
5000
A1
ASYNC
TERMINAL
FEEDER MUX
A3
A4
A5
A6
A2
SYNC
TERMINAL
LOCAL HUB
FEEDER MUX
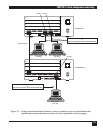
Figure 8-1. This is an example of a local hub in a dual-link, point-to-point network that has been configured
for optimal performance. The lower-numbered channels, A1 and A2, are configured for
interconnect links. Next in priority are mux and X.21 links, followed by sync and async data
channels.