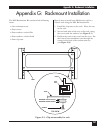
Glossary
255
CPU, central processing unit — The heart (main
processor) of a computer system, or the
computer system itself.
<cr>, carriage return — A user-entered ASCII or
EBCDIC control character used to position the
print mechanism of a printer, or the cursor on a
terminal display, at the left margin.
CRC, cyclic redundancy check — An error-
detection scheme in which the block-check
character is the remainder after dividing all the
serialized bits in a transmission block by a
predetermined binary number. Also, a
polynomial based on the data transmitted.
CSA — A Canadian government agency that
generates standards, conducts tests, and certifies
products to ensure their safety.
CSU, channel service unit — A digital DCE unit for
DDS lines; interfaces with DSU on customer’s
premises.
CTS, clear-to-send — An RS-232 interface control
signal which indicates to a DTE that it may
begin transmitting. Usually issued in response
to RTS.
data — Numbers, text, facts, instructions, and the
like, represented in a formalized manner that
can be manipulated and transmitted by
machines.
data compression — A primary technology built
into the Multiserver products. A block of data is
compressed for transmission and decompressed
upon reception. Fewer bytes are required for
the transfer, thus increasing the data transfer
rate.
data pump — The heart of the modem; its
functions include digital-to-analog and analog-
to-digital conversion, modulation and
demodulation, and interfacing to the digital
and VF lines.
data rate or data signaling rate — A measure of how
quickly data is transmitted. It is best expressed
in bps. It is, however, often incorrectly
expressed in baud. Data rate is synonymous
with speed.
dB, decibel — A comparative (logarithmic)
measure of signal power.
dBm — An absolute measure of signal power, where
0 dBm is equal to one milliwatt into 600 ohms.
DCE, data communications equipment — The
equipment that provides the functions required
to establish, maintain, and terminate a
connection (including signal conversion) for
communications between a DTE and a
telephone line or data circuit. Also, interface
signals typically presented by this equipment.
DC signaling — A configurable signaling option in
an E&M-strapped voice/fax channel. When so
configured, the channel senses the idle/active
status by the DC condition of the M-lead, and
indicates the idle/active status to the remote
end by the DC condition on the E-lead.
DDS, dataphone digital services — A
communications service offered by the
telephone company to transmit data in digital
form.
decadic pulsing — See pulse dialing.
dial-up line, dial line — A circuit or connection on
the public telephone network.
DID, direct inward dialing — A service offered by
the telephone company allowing an outside
caller to dial an internal extension without
passing through the operator. Billing does not
start until the extension answers.
digital loopback — A diagnostic test that forms the
loop at the modem’s DTE interface.
DISA, direct inward system access — A service
offered by a PBX which allows incoming calls to
the PBX to have dialing access within the
private network. It may often be protected by a
dialed password. Billing starts when the PBX
provides the dial tone.
disconnect supervision — Indicates to the local user
that the remote end has gone off-hook. This
protocol is significant in loop start, where
disconnect is denoted by removal of power to
the station equipment.