Spanning Tree Protocol
D-8 Compaq ProLiant BL p-Class GbE Interconnect Switch User Guide
COMPAQ CONFIDENTIAL Codename: Vanilla Part Number: 263680-001 Last Saved On: 4/23/02 10:15 AM
Troubleshooting STP
This section describes several troubleshooting tips.
Spanning Tree Protocol Failure
A failure in the STP generally leads to a bridging loop. A bridging loop in an STP
environment comes from a port that should be in the blocking state, but is forwarding
packets.
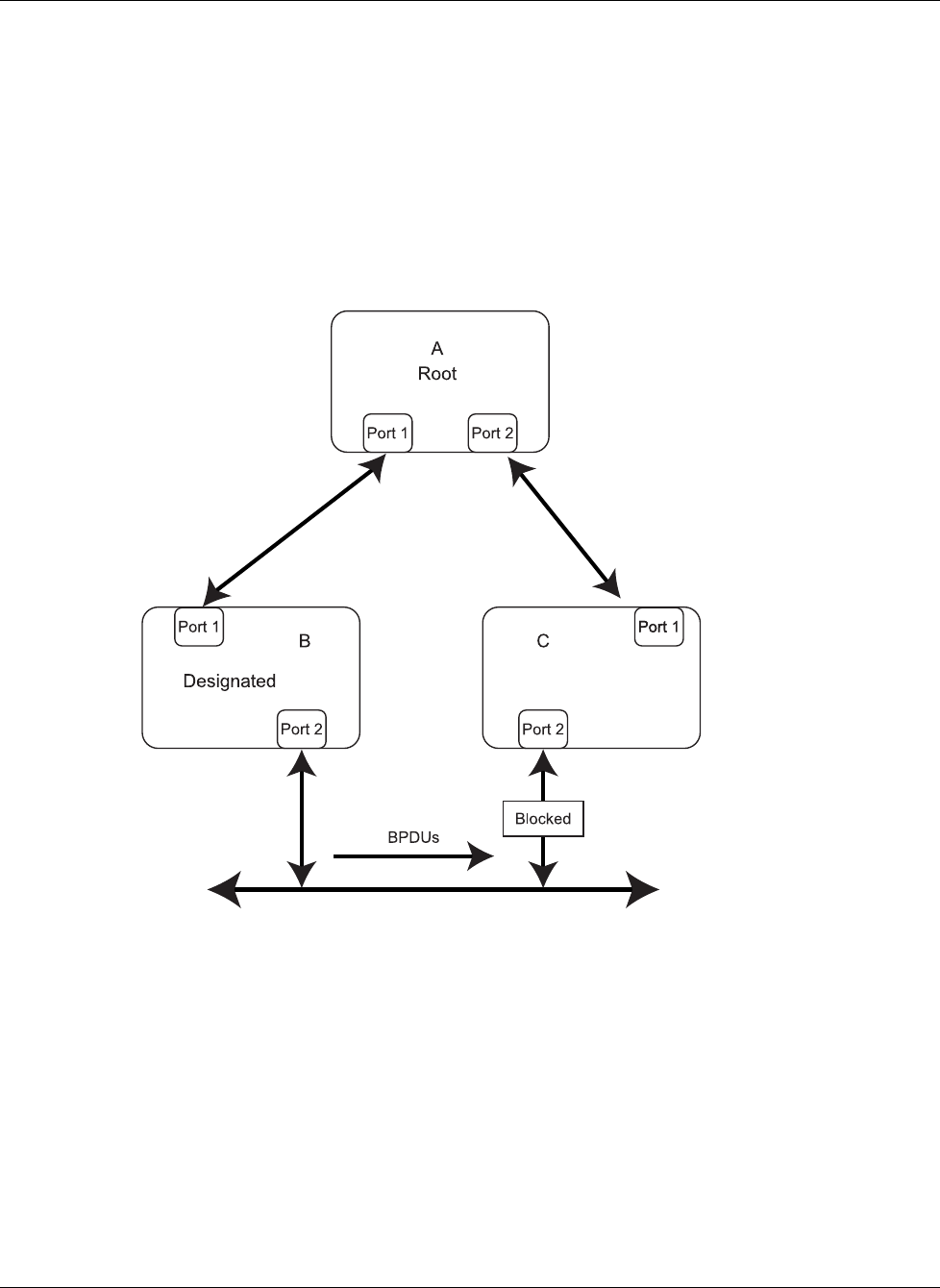
Figure D-6: Example of Spanning Tree Protocol failure
In the example, switch B has been elected as the designated bridge, and port 2 on switch C is
in the blocking state. The election of switch B as the designated bridge is determined by the
exchange of BPDUs between switches B and C. Switch B continues sending BPDUs
advertising its superiority over the other bridges on the LAN. If switch C fails to receive these
BPDUs for longer than the Max Age (default of 20 seconds), it could start to transition its
port 2 from the blocking state to the forwarding state.
IMPORTANT: A port must continue to receive BPDUs advertising superior paths to remain in the
blocking state.