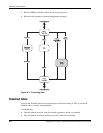
Spanning Tree Protocol
Compaq ProLiant BL p-Class GbE Interconnect Switch User Guide D-11
COMPAQ CONFIDENTIAL Codename: Vanilla Part Number: 263680-001 Last Saved On: 4/23/02 10:15 AM
Resource Errors
The ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch performs its switching and routing
functions primarily in hardware, using specialized ASICs. STP is implemented in software so
it relies on the speed of the processor and other factors to converge. If the processor is
overutilized, the BPDUs may not be sent in a timely fashion. STP generally is not processor
intensive and is given priority over other processes, so this type of error is rare.
Very low values for the Max Age and the Forward Delay can result in an unstable spanning
tree. The loss of BPDUs can lead to data loops.
The diameter of the network can also cause problems. The default values for STP give a
maximum network diameter of seven hops. This means that two switches in the network
cannot be more than seven hops apart. Part of this diameter restriction is the BPDU age field.
As BPDUs are propagated from the root bridge to the leaves of the spanning tree, each bridge
increments the age field. When this field is beyond the maximum age, the packet is discarded.
For large diameter networks, STP convergence can be very slow.
Identifying a Data Loop
Broadcast storms have a similar effect on the network to data loops, but broadcast storm
controls in modern switches (along with subnetting and other network practices) have been
very effective in controlling broadcast storms. The best way to determine if a data loop exists
is to capture traffic on a saturated link and check if similar packets are seen multiple times.
Generally, if all the users of a given domain are having trouble connecting to the network at
the same time, a data loop can be suspected. The port utilization data in the console of the
switch will show unusually high values in this case.
The priority for most loop situations is to restore connectivity as soon as possible. The
simplest remedy is to manually disable all of the ports that provide redundant links. If time
allows, disabling the ports one at a time, and then checking for a restoration of the user’s
connectivity will identify the link that is causing the problem. Connectivity will be restored
immediately after disabling a data loop.