point to the file to be loaded. These variables contain application-specific data that is passed
directly to the EFI application. EFI variables provides system firmware with a boot menu that
points to all the operating systems, even multiple versions of the same operating system.
The EFI Boot Manager enables you to control the server boot environment. Depending on boot
option configuration after the server is powered up, the Boot Manager presents you with different
ways to bring up the system. For example, you can boot to the EFI Shell, to an operating system
located on the network or residing on media in the server, or to the EFI Boot Maintenance
menu.
The following options are available in the EFI Boot Manager menu:
• Boot from a File—Automatically adds EFI applications as boot options or enables you to
boot from a specific file. When you select this option, the system searches for an EFI directory.
If the EFI directory is found, then it looks in each of the subdirectories below EFI. In each
of those subdirectories, it looks for the first file that is an executable EFI application. Each
of the EFI applications that meet this criterion can be automatically added as a boot option.
In addition, legacy boot options for A: and C: are also added if those devices are present.
You can also launch a specific application without adding it as a boot option. In this case,
the EFI Boot Manager searches the root directories and the \EFI\TOOLS directories of all
of the EFI system partitions present in the system for the specified EFI application.
• Add a Boot Option—Adds a boot option to the EFI Boot Manager. Specify the boot option
by providing the name of the EFI application. Along with the name, you can also provide
either ASCII or UNICODE arguments the file uses. Given the EFI application name and any
options, the EFI Boot Manager searches for the executable file in the same directories as
described in the Boot from a File option. When the file is found, it is executed.
• Delete Boot Options—Deletes a specific boot option or all boot options.
• Change Boot Order—Controls the relative order in which the EFI Boot Manager attempts
to execute boot options. For help on the control key sequences you need for this option, see
the help menu.
• Manage BootNext Setting—Selects a boot option to use only once (the next boot operation).
• Set Automatic Boot Timeout—Defines the value in seconds before the system automatically
boots without user intervention. Set this value to zero to disable the timeout feature.
• Exit—Returns control to the EFI Boot Manager menu. This displays the active boot devices,
including a possible integrated shell (if the implementation is so constructed).
For more information, see “Using the Boot Option Maintenance Menu” (page 343).
EFI Commands
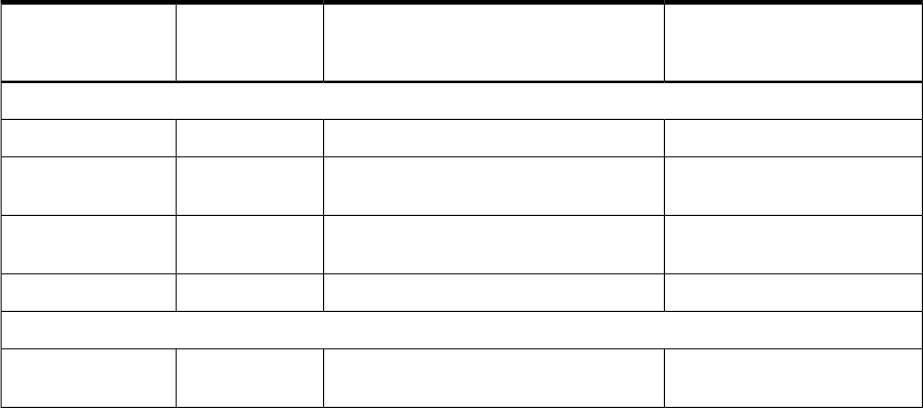
Table D-1 lists EFI commands for the server.
Table D-1 EFI Commands
DefinitionBCH Command Parameters (PA-RISC)BCH Command
Equivalent
(PA-RISC)
EFI Shell Command
These commands are found in all other menus
Boot from specified path[PRI | HAA | ALT | <path>]Bootinfo boot
Display help for specified
command or menu
[<menu> | <command>]HElphelp <command>
Reset the server (to allow
reconfiguration of complex
RESETreset
Return to the main menuMAinexit (at EFI Shell)
MAin
Display or modify a path[PRI | HAA | ALT | CON | KEY | <path>]PAthEFI Boot Manager
“change boot order”
318 Utilities


















