Protocols — Bootable Image Support
Version 1.10 12/01/02 11-15
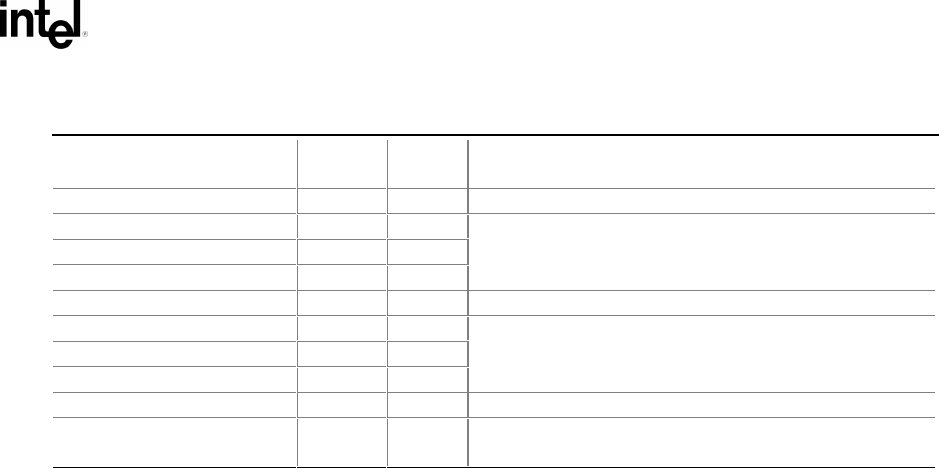
Table 11-7. PMBR Entry to Precede a GUID Partition Table Header
Mnemonic
Byte
Offset
Byte
Length
Description
Boot Indicator 0 1 Must be set to zero to indicate nonbootable partition.
Start Head 1 1
Start Sector 2 1
Start Track 3 1
Set to match the Starting LBA of the EFI Partition
structure. Must be set to 0xFFFFFF if it is not possible
to represent the starting LBA.
OS Type 4 1 Must be 0xEE.
End head 5 1
End Sector 6 1
End Track 7 1
Set to match the Ending LBA of the EFI Partition
structure. Must be set to 0xFFFFFF if it is not possible
to represent the starting LBA.
Starting LBA 8 4 Must be 1 by definition.
Size In LBA 12 4 Length of EFI Partition Head, 0xFFFFFFFF if this value
overflows.
11.2.3 Media Formats
This section describes how booting from different types of removable media is handled. In general
the rules are consistent regardless of a media’s physical type and whether it is removable or not.
11.2.3.1 Removable Media
Removable media may contain a standard FAT12, FAT16, or FAT32 file system. Legacy 1.44 MB
floppy devices typically support a FAT12 file system.
Booting from a removable media device can be accomplished the same way as any other boot. The
boot file path provided to the boot manager can consist of an EFI application image to load, or can
merely be the path to a removable media device. In the first case, the path clearly indicates the
image that is to be loaded. In the later case, the boot manager implements the policy to load the
default application image from the device.
For removable media to be bootable under EFI, it must be built in accordance with the rules laid
out in Section 3.4.1.1.
11.2.3.2 Diskette
EFI bootable diskettes follow the standard formatting conventions used on Intel architecture
personal computers. The diskette contains only a single partition that complies to the EFI file
system type. For diskettes to be bootable under EFI, it must be built in accordance with the rules
laid out in Section 3.4.1.1.
Since the EFI file system definition does not use the code in the first block of the diskette, it is
possible to boot Intel architecture personal computers using a diskette that is also formatted as an
EFI bootable removable media device. The inclusion of boot code for Intel architecture personal
computers is optional and not required by EFI.
Diskettes include the legacy 3.5-inch diskette drives as well as the newer larger capacity removable
media drives such as an Iomega
†
Zip
†
, Fujitsu MO, or MKE LS-120/SuperDisk
†
.


















